转载请标明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/airsaid/article/details/54294144
本文出自:周游的博客
在前面的博客当中,我们学习了 View 的1些工作原理知识等,现在是时候来写1波实例了,毕竟实践出真知嘛~ 在开始写实例之前,首先来了解下自定义 View 到底有哪几种吧,然后再根据每种分别写1个简单的小栗子。
在我们准备编写1个自定义 View 的时候,我们需要根据我们的需求来编写不同的自定义 View。比如说,如果只是想对 TextView 进行扩大,那末可以继承自 TextView 来编写1个新的 View,如果想自己定义1个不同的布局,那末可以继承 ViewGroup 来实现。那末到底有多少类的自定义 View 呢?在网上搜了下,发现大都是说3种、或4种,感觉自定义 View 的分类标准其实不1,在这里的话还是以主席的为准分为4类吧,感觉更细分1些,这4类分别是:
当我们需要实现的效果是1个不规则效果的时候,那末这时候就需要继承 View 来实现了,我们需要重写 onDraw 方法,在该方法里实现各种不规则的图形和效果。当我们使用这类方式的时候,需要自己去处理 warp_content 和 padding。
当系统所提供的 LinearLayout、FrameLayout 等布局控件没法满足我们的需求时,这时候我们就需要使用这类方式来实现自己想要的布局效果了。当我们使用这类方式的时候,需要重写 onLayout 方法来对子 View 进行布局,和丈量本身和子 View 宽高,还需要处理本身的 padding 和子 View 的 margin。
当我们需要基于已有的 View 进行扩大或修改的时候,那末就能够使用这类方式。比如说,我们需要1个圆角的 ImageView,那末这时候就能够继承 ImageView 进行修改了。当我们使用这类方式的时候,1般不需要自己去处理 wrap_content 和 padding 等,由于系统控件已帮我们做好了。
这类方式也叫做:自定义组合 View。该方式比较简单,当我们需要将1组 View 组合在1起,方便后期复用的时候,就能够使用该方法。当我们使用这类方式的时候,不需要去处理 ViewGroup 的丈量和布局流程,由于系统控件已帮我们做好了。
上面我们了解了自定义 View 的4种分类,下面我们分别写4个与分类对应的小栗子来了解下其各自的写法,和1些需要注意的问题。
当我们自定义 View 继承子 View 时,我们需要注意的细节有:
在这个实例当中,我们只需简单的画1个圆便可。重点是细节上的处理,写出1个规范的自定义 View。
实例代码以下:
public class CircleView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
/** 圆半径 */
private float mRadius = 50;
public CircleView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init() {
// 初始化画笔
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int width = getWidth();
int height = getHeight();
canvas.drawCircle(width / 2, height / 2, mRadius, mPaint);
}
}上面的自定义 View 实例很简单,就是绘制了1个圆形。放在布局中,运行看下效果:
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.airsaid.customviewdemo.widget.CircleView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#999999"/>
</RelativeLayout运行结果:
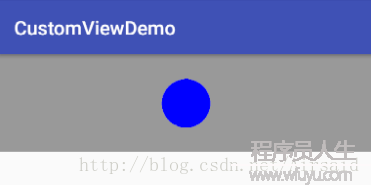
虽然我们已实现了1个简单的继承 View 的自定义 View,但该自定义 View 还不是1个规范的自定义 View,比如此时我们把布局改动1下,将 View 的宽高改成 wrap_content 和增加 padding 和 margin 属性:
<com.airsaid.customviewdemo.widget.CircleView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:background="#999999"
android:padding="15dp"/>重新运行结果:
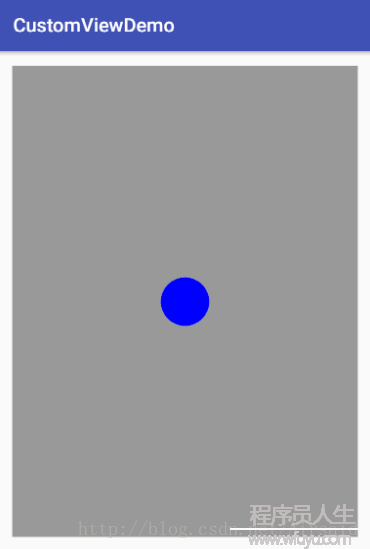
可以看到,虽然我们重新修改了宽高 为 wrap_content,和增加了 padding 和 margin ,但是终究生效的只有 margin。其他的1概没有生效,而 wrap_content 居然和 match_parent 1样。这是怎样1回事呢?
这是由于,margin 是由父控件来控制的,所以我们不需要进行处理,但是我们需要对 View 的 padding 和 LayoutParams 是 wrap_content 的情况进行处理,否则 padding 将会没法生效、wrap_content 的效果会和 match_parent 1样,具体产生这样的缘由可以看深入理解 MeasureSpec这篇文章。
下面我们重写修改下,在 onDraw 绘制时,加上 padding 值,代码以下:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
int width = getWidth() - paddingLeft - paddingRight;
int height = getHeight() - paddingTop - paddingBottom;
canvas.drawCircle(width / 2 + paddingLeft, height / 2 + paddingTop, mRadius, mPaint);
}重写 onMeasure 方法,判断当是 wrap_content 的情况时,自己丈量 View 的宽或高:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
widthSize = (int) (mRadius * 2 + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight());
}
if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
heightSize = (int) (mRadius * 2 + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom());
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
}重新运行:

可以看到,padding 和 wrap_content 都已生效了,这时候候才是1个规范的自定义 View,但是此时这个自定义 View 其实不完善,下篇在自定义属性文章中将会完善它,给它加入自定义属性。
当我们自定义 View 继承自 ViewGroup 时,就需要去实现 onLayout 方法来指定子 View 的摆放位置,并且需要重写 onMeasure 方法来丈量大小。在这个实例当中,我们简单模仿下 LinearLayout ,只不过只实现其 Vertical 模式,在这个实例当中,我们需要注意的细节有:
作为1个规范的自定义 ViewGroup ,这几个细节我们都需要去处理,下面直接上代码:
/**
* 作者: 周游
* 时间: 2017/1/8
* 博客: http://blog.csdn.net/airsaid
* 描写: 1个继承 ViewGroup 的自定义 View 入门实例,该 ViewGroup 垂直摆放子 View。
*/
public class SimpleVerticalLayout extends ViewGroup {
private final Context mContext;
public SimpleVerticalLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public SimpleVerticalLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public SimpleVerticalLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mContext = context;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 获得 ViewGroup 的丈量模式、大小。
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 获得 ViewGroup 的 padding 值
int pl = getPaddingLeft();
int pt = getPaddingTop();
int pr = getPaddingRight();
int pb = getPaddingBottom();
// 丈量所有子 View,当丈量后才能获得到子 View 的丈量宽高
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 自己计算的 ViewGroup 的宽高
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
// 判断如果 ViewGroup 的宽度是 wrap_content
if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
// 计算 ViewGroup 的宽度,遍历所有子 View,最宽的那个 View 的宽度就是 ViewGroup 的宽度
int maxWidth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childAt = getChildAt(i);
if(childAt.getVisibility() == View.GONE){
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childAt.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = childAt.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
maxWidth = childWidth > maxWidth ? childWidth : maxWidth;
}
width = maxWidth + pl + pr;
}
// 判断如果 ViewGroup 的高度是 wrap_content
if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
// 计算 ViewGroup 的高度,由因而垂直摆放,所以高度为每一个子 View 的高度和
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childAt = getChildAt(i);
if(childAt.getVisibility() == View.GONE){
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childAt.getLayoutParams();
height += childAt.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
}
height = height + pt + pb;
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST ? width : widthSize
, heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST ? height : heightSize);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int pl = getPaddingLeft();
int pt = getPaddingTop();
int pr = getPaddingRight();
int pb = getPaddingBottom();
int cl = 0;
int ct = 0;
int cr = 0;
int cb = 0;
int bm = 0;
// 遍历所有子 View
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
// 获得子 View
View childAt = getChildAt(i);
// 判断当子 View 没有 Gone 掉时
if(childAt.getVisibility() != View.GONE){
// 计算每一个子 View 的位置
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childAt.getLayoutParams();
cl = lp.leftMargin;
ct += lp.topMargin;
cr = childAt.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin;
cb += childAt.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin;
// 对子 View 进行布局
childAt.layout(cl + pl, ct + pt + bm, cr + pr, cb + pb + bm);
ct += childAt.getMeasuredHeight();
bm += lp.bottomMargin;
}
}
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(mContext, attrs);
}
}上面的代码实现的很简单,并且注释也很详细。我们直接放到布局中看看效果:
<com.airsaid.customviewdemo.widget.SimpleVerticalLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#999999"
android:padding="10dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:text="我是第1个子 View"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ffff00"
android:text="我是第2个子 View"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ffffff"
android:text="我是第3个子 View"/>
</com.airsaid.customviewdemo.widget.SimpleVerticalLayout>运行结果:

可以看到,SimpleVerticalLayout 的 padding,和子 View 的 margin 都是生效的。
当我们自定义 View 继承自系统已有 View 时,1般是基于其原有功能进行扩大或修改。比如这个实例当中,我们对原本的 EditText 进行扩大,增加1个有内容时显示删除按钮,点击按钮清空文本的 EditText,实例很简单,仍然直接贴代码了:
/**
* 作者: 周游
* 时间: 2017/1/9
* 博客: http://blog.csdn.net/airsaid
* 描写: 1个继承已有 View 的自定义 View 实例,带清除按钮的 EditText。
*/
public class CleanEditText extends EditText{
private final Context mContext;
private Drawable mDeleteDrawable;
public CleanEditText(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CleanEditText(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CleanEditText(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mContext = context;
// 设置右边删除图标
mDeleteDrawable = getResources().getDrawable(R.mipmap.ic_delete);
// 添加监听
addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
setDeleteDrawable();
}
});
setDeleteDrawable();
}
private void setDeleteDrawable() {
setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(null, null, length() > 0 ? mDeleteDrawable : null, null);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP){
if(mDeleteDrawable != null){
int rawX = (int) event.getRawX();
int rawY = (int) event.getRawY();
Rect rect = new Rect();
getGlobalVisibleRect(rect);
rect.left = rect.right - 50;
if(rect.contains(rawX, rawY))
setText("");
}
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}运行结果:

这类自定义 View 的实现方式也叫做:“自定义组合控件”,是1种比较简单的自定义 View 方式。使用这类方式时,由因而继承已有的系统控件,所以我们不需去丈量、布局、处理 margin、padding等,由于系统控件本身已处理好了。
当我们的项目中有1些布局在很多地方都要用到的话,那末第1时间肯定就要想到复用了。复用的话,有人可能会想到使用 include 复用布局,但是如果这样的话,当布局改动性很大时,使用 include 其实不是很灵活。这时候候,就能够使用 ”继承已有 ViewGroup“ 这类方式了。
下面1个实例,就拿我们平时可能常常要写的 Item 为例吧:
/**
* 作者: 周游
* 时间: 2017/1/9
* 博客: http://blog.csdn.net/airsaid
* 描写: 1个继承已有 ViewGroup 的自定义 View 实例,经常使用 item 布局。
*/
public class CustomItemLayout extends FrameLayout {
private TextView mTxtLeft;
private TextView mTxtRight;
private ImageView mImgRight;
private Context mContext;
// 左边文字
private String mLeftText;
// 右边文字
private String mRightText;
// 右边文字色彩
private int mRightTextColor = Color.parseColor("#666666");
// 右边图片
private int mRightImageId = R.mipmap.ic_arrow_right;
// 左边图片
private Drawable mLeftImage = null;
public CustomItemLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomItemLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomItemLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mContext = context;
initAttrs(attrs);
initView();
setData();
}
private void initAttrs(AttributeSet attrs) {
// 获得自定义属性
TypedArray a = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomItemLayout);
mLeftText = a.getString(R.styleable.CustomItemLayout_item_leftText);
mRightText = a.getString(R.styleable.CustomItemLayout_item_rightText);
mRightTextColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.CustomItemLayout_item_rightTextColor, mRightTextColor);
mRightImageId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.CustomItemLayout_item_rightImage, mRightImageId);
mLeftImage = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.CustomItemLayout_item_leftImage);
a.recycle();
}
private void initView() {
// 加载自定义布局到当前 ViewGroup
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(R.layout.view_custom_item_layout, this);
mTxtLeft = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txt_left);
mTxtRight = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txt_right);
mImgRight = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img_right);
}
private void setData() {
if(mLeftText != null) mTxtLeft.setText(mLeftText);
if(mRightText != null) mTxtRight.setText(mRightText);
setRightImage(mRightImageId);
if(mLeftImage != null)
mLeftImage.setBounds(0, 0, dp2px(22), dp2px(12));
mTxtLeft.setCompoundDrawables(null, null, mLeftImage, null);
}
public void setRightTextColor(int resId){
mTxtRight.setTextColor(resId);
}
public void setRightText(String text){
mTxtRight.setText(text);
}
public void setRightText(int resId){
mTxtRight.setText(resId);
}
public String getRightText(){
return mTxtRight.getText().toString();
}
public void setLeftImage(int leftImageId){
mLeftImage = getResources().getDrawable(leftImageId);
setData();
}
public void setRightImage(int rightImageId){
if(rightImageId != -1){
mImgRight.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mImgRight.setImageResource(rightImageId);
}else{
mImgRight.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
private int dp2px(float dpValue){
return (int)(dpValue * (getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density) + 0.5f);
}
}首先自定义1个类,继承自 FrameLayout,固然,这里你也能够选择继承 LinearLayout 或其他,根据具体需求来。其中在构造中获得了自定义属性,和填充了布局。自定义属性有不懂的同学可以先疏忽,下篇会单独拿出来写1篇。
最主要的地方就是填充布局那里,将布局填充到了当前控件也就是自定义的 ViewGroup 上。填充的布局以下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf⑻"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="?android:selectableItemBackground"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:padding="15dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_left"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawablePadding="5dp"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:maxLines="1"
android:textColor="@color/text_black"
android:textSize="@dimen/txt14"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_right"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:gravity="right"
android:maxLines="1"
android:textSize="@dimen/txt14"/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img_right"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_arrow_right"/>
</LinearLayout>使用时,可以直接在布局中通过自定义属性设置数据:
<com.airsaid.customviewdemo.widget.CustomItemLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:item_leftText="版本更新"
app:item_rightImage="@mipmap/ic_arrow_right"
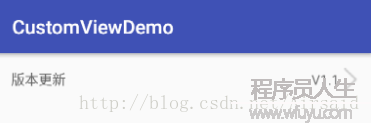
app:item_rightText="V1.1"/>也能够通过暴露的方法设置数据,怎样方便怎样来。
运行结果:
CSDN:http://download.csdn.net/detail/airsaid/9733175
