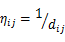ACO蚁群算法解决TSP旅行商问题
来源:程序员人生 发布时间:2015-05-25 09:28:43 阅读次数:3544次
前言
蚁群算法也是1种利用了大自然规律的启发式算法,与之前学习过的GA遗传算法类似,遗传算法是用了生物进行理论,把更具适应性的基因传给下1代,最后就可以得到1个最优解,常经常使用来寻觅问题的最优解。固然,本篇文章不会主讲GA算法的,想要了解的同学可以查看,我的遗传算法学习和遗传算法在走迷宫中的应用。话题重新回到蚁群算法,蚁群算法是1个利用了蚂蚁寻觅食品的原理。不知道小时候有无发现,当1个蚂蚁发现了地上的食品,然后非常迅速的,就有其他的蚂蚁集合过来,最后把食品抬回家,这里面其实有着非常多的道理的,在ACO中就用到了这个机理用于解决实际生活中的1些问题。
蚂蚁找食品
首先我们要具体说说1个成心思的事情,就是蚂蚁找食品的问题,理解了这个原理以后,对理解ACO算法就非常容易了。蚂蚁作为那末小的动物,在地上漫无目的的寻觅食品,起初都是没有目标的,他从蚂蚁洞中走出,随机的爬向各个方向,在这期间他会向外界播撒1种化学物资,姑且就叫做信息素,所以这里就能够得到的1个条件,越多蚂蚁走过的路径,信息素浓度就会越高,那末某条路径信息素浓度高了,自然就会有越多的蚂蚁感觉到了,就集聚集过来了。所以当众多蚂蚁中的1个找到食品以后,他就会在走过的路径中放出信息素浓度,因此就会有很多的蚂蚁赶来了。类似下面的场景:
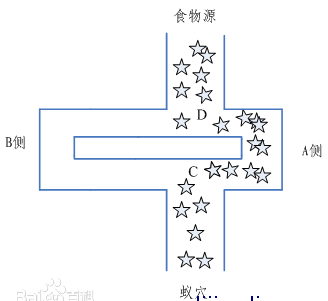
至于蚂蚁是如何感知这个信息素,这个就得问生物学家了,我也没做过研究。
算法介绍
OK,有了上面这个自然生活中的生物场景以后,我们再来切入文章主题来学习1下蚁群算法,百度百科中对应蚁群算法是这么介绍的:蚁群算法是1种在图中寻觅优化路径的机率型算法。他的灵感就是来自于蚂蚁发现食品的行动。蚁群算法是1种新的摹拟进化优化的算法,与遗传算法有很多相似的地方。蚁群算法在比较早的时候成功解决了TSP旅行商的问题(在后面的例子中也会以这个例子)。要用算法去摹拟蚂蚁的这类行动,关键在于信息素的在算法中的设计,和路径中信息素浓度越大的路径,将会有更高的几率被蚂蚁所选择到。
算法原理
要想实现上面的几个摹拟行动,需要借助几个公式,固然公式不是我自己定义的,主要有3个,以下图:

上图中所出现的alpha,beita,p等数字都是控制因子,所以可没必要理睬,Tij(n)的意思是在时间为n的时候,从城市i到城市j的路径的信息素浓度。类似于nij的字母是城市i到城市j距离的倒数。就是下面这个公式。
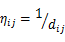
所以所有的公式都是为第1个公式服务的,第1个公式的意思是指第k只蚂蚁选择从城市i到城市j的几率,可以见得,这个受距离和信息素浓度的两重影响,距离越远,去此城市的几率自然也低,所以nij会等于距离的倒数,而且在算信息素浓度的时候,也斟酌到了信息素浓度衰减的问题,所以会在上次的浓度值上乘以1个衰减因子P。另外还要加上本轮搜索增加的信息素浓度(假设有蚂蚁经过此路径的话),所以这几个公式的整体设计思想还是非常棒的。
算法的代码实现
由于本身我这里没有甚么真实的测试数据,就随意自己构造了1个简单的数据,输入以下,分为城市名称和城市之间的距离,用#符号做辨别标识,大家应当可以看得懂吧
# CityName
1
2
3
4
# Distance
1 2 1
1 3 1.4
1 4 1
2 3 1
2 4 1
3 4 1
蚂蚁类Ant.java:
package DataMining_ACO;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 蚂蚁类,进行路径搜索的载体
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Ant implements Comparable<Ant> {
// 蚂蚁当前所在城市
String currentPos;
// 蚂蚁遍历完回到原点所用的总距离
Double sumDistance;
// 城市间的信息素浓度矩阵,随着时间的增多而减少
double[][] pheromoneMatrix;
// 蚂蚁已走过的城市集合
ArrayList<String> visitedCitys;
// 还未走过的城市集合
ArrayList<String> nonVisitedCitys;
// 蚂蚁当前走过的路径
ArrayList<String> currentPath;
public Ant(double[][] pheromoneMatrix, ArrayList<String> nonVisitedCitys) {
this.pheromoneMatrix = pheromoneMatrix;
this.nonVisitedCitys = nonVisitedCitys;
this.visitedCitys = new ArrayList<>();
this.currentPath = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* 计算路径的总本钱(距离)
*
* @return
*/
public double calSumDistance() {
sumDistance = 0.0;
String lastCity;
String currentCity;
for (int i = 0; i < currentPath.size() - 1; i++) {
lastCity = currentPath.get(i);
currentCity = currentPath.get(i + 1);
// 通过距离矩阵进行计算
sumDistance += ACOTool.disMatrix[Integer.parseInt(lastCity)][Integer
.parseInt(currentCity)];
}
return sumDistance;
}
/**
* 蚂蚁选择前往下1个城市
*
* @param city
* 所选的城市
*/
public void goToNextCity(String city) {
this.currentPath.add(city);
this.currentPos = city;
this.nonVisitedCitys.remove(city);
this.visitedCitys.add(city);
}
/**
* 判断蚂蚁是不是已又重新回到出发点
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isBack() {
boolean isBack = false;
String startPos;
String endPos;
if (currentPath.size() == 0) {
return isBack;
}
startPos = currentPath.get(0);
endPos = currentPath.get(currentPath.size() - 1);
if (currentPath.size() > 1 && startPos.equals(endPos)) {
isBack = true;
}
return isBack;
}
/**
* 判断蚂蚁在本次的走过的路径中是不是包括从城市i到城市j
*
* @param cityI
* 城市I
* @param cityJ
* 城市J
* @return
*/
public boolean pathContained(String cityI, String cityJ) {
String lastCity;
String currentCity;
boolean isContained = false;
for (int i = 0; i < currentPath.size() - 1; i++) {
lastCity = currentPath.get(i);
currentCity = currentPath.get(i + 1);
// 如果某1段路径的始末位置1致,则认为有经过此城市
if ((lastCity.equals(cityI) && currentCity.equals(cityJ))
|| (lastCity.equals(cityJ) && currentCity.equals(cityI))) {
isContained = true;
break;
}
}
return isContained;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Ant o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.sumDistance.compareTo(o.sumDistance);
}
}
蚁群算法工具类ACOTool.java:
package DataMining_ACO;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 蚁群算法工具类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class ACOTool {
// 输入数据类型
public static final int INPUT_CITY_NAME = 1;
public static final int INPUT_CITY_DIS = 2;
// 城市间距离邻接矩阵
public static double[][] disMatrix;
// 当前时间
public static int currentTime;
// 测试数据地址
private String filePath;
// 蚂蚁数量
private int antNum;
// 控制参数
private double alpha;
private double beita;
private double p;
private double Q;
// 随机数产生器
private Random random;
// 城市名称集合,这里为了方便,将城市用数字表示
private ArrayList<String> totalCitys;
// 所有的蚂蚁集合
private ArrayList<Ant> totalAnts;
// 城市间的信息素浓度矩阵,随着时间的增多而减少
private double[][] pheromoneMatrix;
// 目标的最短路径,顺序为从集合的前部往后移动
private ArrayList<String> bestPath;
// 信息素矩阵存储图,key采取的格式(i,j,t)->value
private Map<String, Double> pheromoneTimeMap;
public ACOTool(String filePath, int antNum, double alpha, double beita,
double p, double Q) {
this.filePath = filePath;
this.antNum = antNum;
this.alpha = alpha;
this.beita = beita;
this.p = p;
this.Q = Q;
this.currentTime = 0;
readDataFile();
}
/**
* 从文件中读取数据
*/
private void readDataFile() {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
int flag = ⑴;
int src = 0;
int des = 0;
int size = 0;
// 进行城市名称种数的统计
this.totalCitys = new ArrayList<>();
for (String[] array : dataArray) {
if (array[0].equals("#") && totalCitys.size() == 0) {
flag = INPUT_CITY_NAME;
continue;
} else if (array[0].equals("#") && totalCitys.size() > 0) {
size = totalCitys.size();
// 初始化距离矩阵
this.disMatrix = new double[size + 1][size + 1];
this.pheromoneMatrix = new double[size + 1][size + 1];
// 初始值⑴代表此对应位置无值
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
this.disMatrix[i][j] = ⑴;
this.pheromoneMatrix[i][j] = ⑴;
}
}
flag = INPUT_CITY_DIS;
continue;
}
if (flag == INPUT_CITY_NAME) {
this.totalCitys.add(array[0]);
} else {
src = Integer.parseInt(array[0]);
des = Integer.parseInt(array[1]);
this.disMatrix[src][des] = Double.parseDouble(array[2]);
this.disMatrix[des][src] = Double.parseDouble(array[2]);
}
}
}
/**
* 计算从蚂蚁城市i到j的几率
*
* @param cityI
* 城市I
* @param cityJ
* 城市J
* @param currentTime
* 当前时间
* @return
*/
private double calIToJProbably(String cityI, String cityJ, int currentTime) {
double pro = 0;
double n = 0;
double pheromone;
int i;
int j;
i = Integer.parseInt(cityI);
j = Integer.parseInt(cityJ);
pheromone = getPheromone(currentTime, cityI, cityJ);
n = 1.0 / disMatrix[i][j];
if (pheromone == 0) {
pheromone = 1;
}
pro = Math.pow(n, alpha) * Math.pow(pheromone, beita);
return pro;
}
/**
* 计算综合几率蚂蚁从I城市走到J城市的几率
*
* @return
*/
public String selectAntNextCity(Ant ant, int currentTime) {
double randomNum;
double tempPro;
// 总几率指数
double proTotal;
String nextCity = null;
ArrayList<String> allowedCitys;
// 各城市几率集
double[] proArray;
// 如果是刚刚开始的时候,没有途经任何城市,则随机返回1个城市
if (ant.currentPath.size() == 0) {
nextCity = String.valueOf(random.nextInt(totalCitys.size()) + 1);
return nextCity;
} else if (ant.nonVisitedCitys.isEmpty()) {
// 如果全部遍历终了,则再次回到出发点
nextCity = ant.currentPath.get(0);
return nextCity;
}
proTotal = 0;
allowedCitys = ant.nonVisitedCitys;
proArray = new double[allowedCitys.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < allowedCitys.size(); i++) {
nextCity = allowedCitys.get(i);
proArray[i] = calIToJProbably(ant.currentPos, nextCity, currentTime);
proTotal += proArray[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < allowedCitys.size(); i++) {
// 归1化处理
proArray[i] /= proTotal;
}
// 用随机数选择下1个城市
randomNum = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
randomNum = randomNum / 100;
// 由于1.0是没法判断到的,,总和会无穷接近1.0取为0.99做判断
if (randomNum == 1) {
randomNum = randomNum - 0.01;
}
tempPro = 0;
// 肯定区间
for (int j = 0; j < allowedCitys.size(); j++) {
if (randomNum > tempPro && randomNum <= tempPro + proArray[j]) {
// 采取拷贝的方式避免援用重复
nextCity = allowedCitys.get(j);
break;
} else {
tempPro += proArray[j];
}
}
return nextCity;
}
/**
* 获得给定时间点上从城市i到城市j的信息素浓度
*
* @param t
* @param cityI
* @param cityJ
* @return
*/
private double getPheromone(int t, String cityI, String cityJ) {
double pheromone = 0;
String key;
// 上1周期需将时间倒回1周期
key = MessageFormat.format("{0},{1},{2}", cityI, cityJ, t);
if (pheromoneTimeMap.containsKey(key)) {
pheromone = pheromoneTimeMap.get(key);
}
return pheromone;
}
/**
* 每轮结束,刷新信息素浓度矩阵
*
* @param t
*/
private void refreshPheromone(int t) {
double pheromone = 0;
// 上1轮周期结束后的信息素浓度,丛信息素浓度图中查找
double lastTimeP = 0;
// 本轮信息素浓度增加量
double addPheromone;
String key;
for (String i : totalCitys) {
for (String j : totalCitys) {
if (!i.equals(j)) {
// 上1周期需将时间倒回1周期
key = MessageFormat.format("{0},{1},{2}", i, j, t - 1);
if (pheromoneTimeMap.containsKey(key)) {
lastTimeP = pheromoneTimeMap.get(key);
} else {
lastTimeP = 0;
}
addPheromone = 0;
for (Ant ant : totalAnts) {
if(ant.pathContained(i, j)){
// 每只蚂蚁传播的信息素为控制因子除以距离总本钱
addPheromone += Q / ant.calSumDistance();
}
}
// 将上次的结果值加上递增的量,并存入图中
pheromone = p * lastTimeP + addPheromone;
key = MessageFormat.format("{0},{1},{2}", i, j, t);
pheromoneTimeMap.put(key, pheromone);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 蚁群算法迭代次数
* @param loopCount
* 具体遍历次数
*/
public void antStartSearching(int loopCount) {
// 蚁群寻觅的总次数
int count = 0;
// 选中的下1个城市
String selectedCity = "";
pheromoneTimeMap = new HashMap<String, Double>();
totalAnts = new ArrayList<>();
random = new Random();
while (count < loopCount) {
initAnts();
while (true) {
for (Ant ant : totalAnts) {
selectedCity = selectAntNextCity(ant, currentTime);
ant.goToNextCity(selectedCity);
}
// 如果已遍历完所有城市,则跳出此轮循环
if (totalAnts.get(0).isBack()) {
break;
}
}
// 周期时间叠加
currentTime++;
refreshPheromone(currentTime);
count++;
}
// 根据距离本钱,选出所花距离最短的1个路径
Collections.sort(totalAnts);
bestPath = totalAnts.get(0).currentPath;
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("经过{0}次循环遍历,终究得出的最好路径:", count));
System.out.print("entrance");
for (String cityName : bestPath) {
System.out.print(MessageFormat.format("-->{0}", cityName));
}
}
/**
* 初始化蚁群操作
*/
private void initAnts() {
Ant tempAnt;
ArrayList<String> nonVisitedCitys;
totalAnts.clear();
// 初始化蚁群
for (int i = 0; i < antNum; i++) {
nonVisitedCitys = (ArrayList<String>) totalCitys.clone();
tempAnt = new Ant(pheromoneMatrix, nonVisitedCitys);
totalAnts.add(tempAnt);
}
}
}
场景测试类Client.java:
package DataMining_ACO;
/**
* 蚁群算法测试类
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args){
//测试数据
String filePath = "C:UserslyqDesktopiconinput.txt";
//蚂蚁数量
int antNum;
//蚁群算法迭代次数
int loopCount;
//控制参数
double alpha;
double beita;
double p;
double Q;
antNum = 3;
alpha = 0.5;
beita = 1;
p = 0.5;
Q = 5;
loopCount = 5;
ACOTool tool = new ACOTool(filePath, antNum, alpha, beita, p, Q);
tool.antStartSearching(loopCount);
}
}
算法的输出,就是在屡次搜索以后,找到的路径中最短的1个路径:
经过5次循环遍历,终究得出的最好路径:
entrance-->4-->1-->2-->3-->4
由于数据量比较小,其实不能看出蚁群算法在这方面的优势,博友们可以再次基础上自行改造,并用大1点的数据做测试,其中的4个控制因子也能够调控。蚁群算法作为1种启发式算法,还可以和遗传算法结合,创造出更优的算法。蚁群算法可以解决许多这样的连通图路径优化问题。但是有的时候也会出现搜索时间太长的问题。
参考文献:百度百科.蚁群算法
我的数据发掘算法库:https://github.com/linyiqun/DataMiningAlgorithm
我的算法库:https://github.com/linyiqun/lyq-algorithms-lib
生活不易,码农辛苦
如果您觉得本网站对您的学习有所帮助,可以手机扫描二维码进行捐赠