[置顶] 看数据结构写代码(37) 图的十字链表的表示与实现
来源:程序员人生 发布时间:2015-04-21 09:16:53 阅读次数:3366次
图的邻接表在 查找 有向图的 出度 很 方便,但是 在 查找 入度 时,需要遍历全部图。如果想要 方便的 查找 入度,需要 建立 逆邻接表。10字链表 正好 就是 邻接表 和 逆邻接表的结合。具体结构图以下:
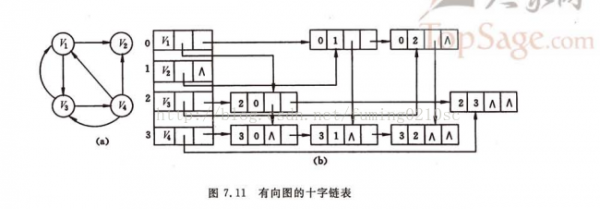
感觉 10字链表 在 查找 入度时 方便 1些,其他 跟 邻接表没甚么区分。
源代码 网盘地址:点击打开链接
代码以下:
// CrossLinkGraph.cpp : 定义控制台利用程序的入口点。
//有向图的10字链表表示法
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#define MAX_VEX_NUM 20
enum E_State
{
E_State_Error = 0,
E_State_Ok = 1,
};
struct ArcNode//弧节点
{
int tailIndex;//弧尾位置
int headIndex;//弧头位置
ArcNode * tailNext;//下1个弧尾相同的弧
ArcNode * headNext;//下1个弧头相同的弧
};
typedef struct VNode
{
char vexName;//顶点名称
ArcNode * firstIn;
ArcNode * firstOut;
}GraphList[MAX_VEX_NUM];//
struct Graph
{
GraphList list;//顶点数组.
int vexNum,arcNum;
};
//获得弧 的 头节点
ArcNode * getHeadNode(){
ArcNode * pNode = (ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if (pNode){
pNode->headIndex = pNode->tailIndex = ⑴;
pNode->headNext = pNode->tailNext = NULL;
}
return pNode;
}
ArcNode * getArcNode(int tailIndex,int headIndex){
ArcNode * pNode = getHeadNode();
if (pNode){
pNode->headIndex = headIndex;
pNode->tailIndex = tailIndex;
}
return pNode;
}
int vexLocation(Graph g,char vex){
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexNum; i++){
if (g.list[i].vexName == vex){
return i;
}
}
return ⑴;
}
void createGrahp(Graph * g){
printf("输入图的顶点数 和 边(弧)数
");
scanf("%d%d%*c",&g->vexNum,&g->arcNum);
//构造顶点集
printf("请输入顶点集
");
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
char name;
scanf("%c",&name);
g->list[i].vexName = name;
g->list[i].firstIn = g->list[i].firstOut = getHeadNode();//建立 头节点,并让头指针指向头节点
}
//构造顶点关系
fflush(stdin);
printf("请输入顶点的关系
");
for (int i = 0; i < g->arcNum; i++){
char vex1,vex2;
scanf("%c%c%*c",&vex1,&vex2);
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
int location2 = vexLocation(*g,vex2);
ArcNode * pNode = getArcNode(location1,location2);
pNode->tailNext = g->list[location1].firstOut->tailNext;
g->list[location1].firstOut->tailNext = pNode;
pNode->headNext = g->list[location2].firstIn->headNext;
g->list[location2].firstIn->headNext = pNode;
}
}
//只要删除所有顶点的弧尾(或弧头)节点便可,
//同时删除弧头弧尾 ,内存毛病
void destoryGraph(Graph * g){
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
ArcNode * next = g->list[i].firstOut;//删除所有弧尾
while (next != NULL){
ArcNode * freeNode = next;
next = next->tailNext;
free(freeNode);
}
g->list[i].firstIn = g->list[i].firstOut = NULL;
g->list[i].vexName = ' ';
g->vexNum = g->arcNum = 0;
}
}
//顶点vex1 和顶点vex2 是不是相邻
bool graphIsAdj(Graph g,char vex1,char vex2){
int location = vexLocation(g,vex1);
ArcNode * next = g.list[location].firstOut->tailNext;
while (next != NULL){
if (g.list[next->headIndex].vexName == vex2){
return true;
}
next = next->tailNext;
}
return false;
}
int graphDegree(Graph g,char vex){
int degree = 0;
int locaiton = vexLocation(g,vex);
ArcNode * next = g.list[locaiton].firstOut->tailNext;//计算所有出度
while (next != NULL){
degree++;
next = next->tailNext;
}
next = g.list[locaiton].firstIn->headNext;//计算所有入度
while (next != NULL){
degree++;
next = next->headNext;
}
return degree;
}
char firstAdj(Graph g,char vex){
int location = vexLocation(g,vex);
ArcNode * next = g.list[location].firstOut->tailNext;
if (next != NULL)
{
return g.list[next->headIndex].vexName;
}
return ' ';
}
char nextAdj(Graph g,char vex1,char vex2){
int location = vexLocation(g,vex1);
ArcNode * next = g.list[location].firstOut->tailNext;
while (next != NULL){//查找到 vex2
if (g.list[next->headIndex].vexName == vex2){
break;
}
next = next->tailNext;
}
if (next != NULL){
ArcNode * nextNode = next->tailNext;
if (nextNode != NULL){
return g.list[nextNode->headIndex].vexName;
}
}
return ' ';
}
//插入边(弧)
void insertArc(Graph * g,char vex1,char vex2){
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
int location2 = vexLocation(*g,vex2);
ArcNode * node = getArcNode(location1,location2);
node->tailNext = g->list[location1].firstOut->tailNext;
g->list[location1].firstOut->tailNext = node;
node->headNext = g->list[location2].firstIn->headNext;
g->list[location2].firstIn->headNext = node;
g->arcNum ++;
}
//删除边(弧)
void deleteArc(Graph * g,char vex1,char vex2){
g->arcNum--;
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
int location2 = vexLocation(*g,vex2);
ArcNode * next = g->list[location1].firstOut->tailNext;
ArcNode * pre = g->list[location1].firstOut;
while (next != NULL){//在更改 尾部相同的 链表时,不能删除 弧
if (next->headIndex == location2){
pre->tailNext = next->tailNext;
//free(next);
break;
}
pre = next;
next = next->tailNext;
}
next = g->list[location2].firstIn->headNext;
pre = g->list[location2].firstIn;
//在更改弧头相同的链表时,释放空间.
while (next != NULL){
if (next->tailIndex == location1){
pre->headNext = next->headNext;
free(next);
break;
}
pre = next;
next = next->headNext;
}
}
//插入顶点
void insertVex(Graph * g, char vex){
if (g->vexNum < MAX_VEX_NUM){
g->list[g->vexNum].vexName = vex;
g->list[g->vexNum].firstIn = g->list[g->vexNum].firstOut = getHeadNode();
g->vexNum++;
}
}
//删除顶点
void deleteVex(Graph * g,char vex){
int location = vexLocation(*g,vex);
//删除顶点 一样需要 遍历全部 图 查找 与 vex 相干的弧节点
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
ArcNode * next = g->list[i].firstOut->tailNext;
while (next != NULL){
if (next->headIndex == location || next->tailIndex == location){
ArcNode * delNode = next;
next = next->tailNext;
char delData1 = g->list[delNode->tailIndex].vexName;
char delData2 = g->list[delNode->headIndex].vexName;
deleteArc(g,delData1,delData2);
}
else{
next = next->tailNext;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
ArcNode * next = g->list[i].firstOut->tailNext;
while (next != NULL){
if(next->headIndex > location){
next->headIndex --;
}
if(next->tailIndex > location){
next->tailIndex --;
}
next = next->tailNext;
}
}
free(g->list[location].firstIn);//释放头节点
//vex下面的 顶点上移
for (int i = location + 1; i < g->vexNum; i++){
g->list[i⑴] = g->list[i];
}
g->vexNum --;
}
void printGrahp(Graph g){
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexNum; i++){
printf("以%c为弧尾的 顶点有:",g.list[i].vexName);
ArcNode * next = g.list[i].firstOut->tailNext;//删除所有弧尾
while (next != NULL){
printf("%c",g.list[next->headIndex].vexName);
next = next->tailNext;
}
printf("
以%c为弧头的 顶点有:",g.list[i].vexName);
next = g.list[i].firstIn->headNext;//删除所有弧尾
while (next != NULL){
printf("%c",g.list[next->tailIndex].vexName);
next = next->headNext;
}
printf("
");
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Graph g;
createGrahp(&g);
printGrahp(g);
printf("图的顶点数:%d,边(弧)树为:%d
",g.vexNum,g.arcNum);
char * isAdj = graphIsAdj(g,'b','d')? "相邻" : "不相邻";
int degree = graphDegree(g,'d');
char first = firstAdj(g,'c');
char next = nextAdj(g,'d','c');
printf("c的第1个邻接点是%c,d的c邻接点的下1个邻接点是:%c
",first,next);
printf("b 和 d %s,d的度为:%d
",isAdj,degree);
insertVex(&g,'e');
printf("插入e顶点以后图结构以下:
");
printGrahp(g);
insertArc(&g,'a','e');
printf("插入(a,e) 以后图结构以下:
");
printGrahp(g);
deleteArc(&g,'d','c');
printf("删除(d,c)以后图结构以下:
");
printGrahp(g);
deleteVex(&g,'a');
printf("删除顶点a以后图结构以下:
");
printGrahp(g);
printf("图的顶点数:%d,边(弧)数为:%d
",g.vexNum,g.arcNum);
destoryGraph(&g);
return 0;
}
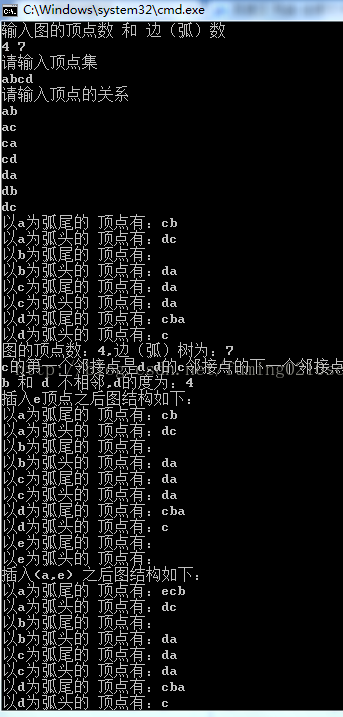
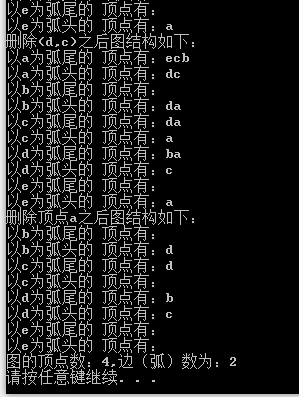
运行截图:
生活不易,码农辛苦
如果您觉得本网站对您的学习有所帮助,可以手机扫描二维码进行捐赠




