Android学习笔记二十二.使用ContentProvider实现数据共享(五).监听ContentProvider的数据改变
来源:程序员人生 发布时间:2015-01-18 10:10:23 阅读次数:3858次
1、使用ContentProvider管理多媒体内容
Android提供了Camera程序来支持拍照、拍摄视频,用户拍摄的相片、视频都将寄存在固定的位置。Android一样为这些多媒体内容提供了ContentProvider,所以我们可以通过使用ContentProvider实现其他利用直接访问Camera所拍摄的照片、视频等。
1.多媒体ContentProvider的Uri
(1)MediaStore.Audio.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI:存储在外部存储器(SD卡)上的音频文件内容的ContentProvider的Uri.
(2)MediaStore.Audio.Media.INTERNAL_CONTENT_URI:存储在手机内部存储器(SD卡)上的音频文件内容的ContentProvider的Uri.
(3)MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI:存储在外部存储器(SD卡)上的图片文件内容的ContentProvider的Uri.
(4)MediaStore.Images.Media.INTERNAL_CONTENT_URI:存储在手机内部存储器(SD卡)上的图片文件内容的ContentProvider的Uri.
(5)MediaStore.Video.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI:存储在外部存储器(SD卡)上的视频文件内容的ContentProvider的Uri.
(6)MediaStore.Video.Media.INTERNAL_CONTENT_URI:存储在手机内部存储器(SD卡)上的视频文件内容的ContentProvider的Uri.
2.ContentResolve相干操作说明
(1)Uri ContentResolver.query(Uri uri, String[]
projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder)
功能:查询给定URI对应的ContentProvider所暴露的数据中与selection相匹配的数据,并返回结果set集合的Cursor对象
参数:
uri :content:// scheme情势的URI,用于获得URI对应的ContentProvider;
projection:返回列表的其中列,当传入值为null时则表示返回表中所有的列(效力低)
selection :声明表中哪些行返回的过滤器,当传入值为null时则表示返回给定URI数据的所有行
selectionArgs 通常为null
sortOrder 选择如何实现所有行排序,当传入值为null时为默许排序,便可能为无序
(2)Uri android.content.ContentResolver.insert(Uri url, ContentValues values)
功能:向URI对应的ContentProvider中插入values对应的数据(向表中插入1行数据)
参数:
url:插入表的URL
values :向给定的URI对应的数据表插入1个数据,为ContentValue对象对应的数据,传递1个空ContentValues将创建1个空行。
返回值:
the URL of the newly created row.
(3)delete(Uri uri,String where,String[] selectionArgs)
功能:删除Uri对应的ContentProvider中where提交匹配的数据
(4)update(Uri uri,ContentValues values,String where,String selectionArgs)
功能:更新Uri对应的ContentProvider中where提交匹配的数据为values对应的数据
3.源码分析
(1)查询1张图片并获得其相应的信息
思路:首先,获得URI对应ContentProvider的数据且为set集合。其次,顺次获得每张图片的相干信息并存入相应的ArrayList表中。
ArrayList<String> names=new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> descs=new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> fileNames=new ArrayList<String>();
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI,null,null,null,null);
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(Media.DISPLAY_NAME)); //a.获得图片的显示名
String desc = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(Media.DESCRIPTION)); //b.获得图片的详细描写
byte[] data = cursor.getBlob(cursor.getColumnIndex(Media.DATA)); //c.获得图片的保存位置的数据
names.add(name); //d将图片名、图片描写、图片保存路径分别添加到names、descs、fileNames集合中
descs.add(desc);
fileNames.add(new String(data,0,data.length⑴));
注意:这里是获得Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI对应数据中的1张图片信息,如果需要获得所有set集合中的数据,则需要while(cursor.moveToNext())对集合中的所有图片数据进行遍历,然后顺次将图片的名称、属性、保存路径分别添加到对应的ArrayList集合中。
(2)创建1个List集合,List集合的元素是Map,并将names、descs两个集合对象的数据转换到Map集合中;创建1个SimpleAdapter,并为show
ListView组件设置Adapter。
private ListView show;
List<Map<String,Object>> listItems = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();
for(int i = 0; i<names.size() ;i++)
{
Map<String,Object> listItem = new HashMap<String,Object>(); //实例化1个HashMap对象
listItem.put("name", names.get(i)); //获得列表中指定位置的元素,元素i的名称
listItem.put("desc", descs.get(i)); //元素i的属性
listItems.add(listItem);
}
SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(
MediaProviderTest.this //上下文
,listItems //map集合数据
,R.layout.line //列表项布局
,new String[] {"name","desc"}//与每一个列表项相干列表中列名字,其被添加到Map集合中
,new int[] {R.id.name,R.id.desc});//对应与"from"列表的列组件,全部为TextView组件
show.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
注释:SimpleAdapter(Context context, List<? extends Map<String, ?>> data, int resource, String[] from, int[] to)
context:SimpleAdapter运行上下文
data :1个列表的Map集合,列表中的每一个条目对应于列表中的1行。Map集合包括每行的数据,并且应当包括“from”中所有指定的条目
resource :1个视图布局的资源标识符,该布局文件最少包括了"to"中的组件,用于定义列表项的视图;
from :A list of column names that will be added to the Map
associated with each item
to :The views that should display column in the "from" parameter.
These should all be TextViews. The first N views in this list are given the values of the first N columns in the from parameter.
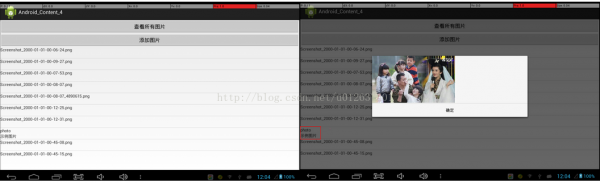
效果演示:
(3)创建1个对话框
a.加载View.xml界面布局代表的视图
b.使用对话框显示用户单击的图片
View viewDialog=getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.view, null);
new AlertDialog.Builder(MediaProviderTest.this)
.setView(viewDialog).setPositiveButton("肯定", null)
.show();
其中,R.layout.view为1个布局文件。
4.源码
(1)MediaProviderTest.java
package com.example.android_content_4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.provider.MediaStore.Images.Media;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
public class MediaProviderTest extends Activity {
private Button catBtn,addBtn;
private ListView show;
ArrayList<String> names=new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> descs=new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> fileNames=new ArrayList<String>();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
catBtn=(Button)findViewById(R.id.cat);
addBtn=(Button)findViewById(R.id.add);
show=(ListView)findViewById(R.id.list);
catBtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
names.clear();
descs.clear();
fileNames.clear();
//1.通过ContentResolver查询所有图片信息
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI,null,null,null,null);
while(cursor.moveToNext())
{
//a.获得图片的显示名
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(Media.DISPLAY_NAME));
//b.获得图片的详细描写
String desc = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(Media.DESCRIPTION));
//c.获得图片的保存位置的数据
byte[] data = cursor.getBlob(cursor.getColumnIndex(Media.DATA));
//d.将图片名、图片描写、图片保存路径分别添加到names、descs、fileNames集合中
names.add(name);
descs.add(desc);
fileNames.add(new String(data,0,data.length⑴));
}
//2.创建1个List集合,List集合的元素是Map,并将names、descs两个集合对象的数据转换到Map集合中
List<Map<String,Object>> listItems = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();
for(int i = 0; i<names.size() ;i++)
{
Map<String,Object> listItem = new HashMap<String,Object>();
listItem.put("name", names.get(i)); //获得列表中指定位置的元素,元素i的名称
listItem.put("desc", descs.get(i)); //元素i的属性
listItems.add(listItem);
}
//3.创建1个SimpleAdapter,并为show ListView组件设置Adapter
SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(
MediaProviderTest.this,listItems
,R.layout.line
,new String[] {"name","desc"}
,new int[] {R.id.name,R.id.desc});
show.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
}
});
//4.为show ListView的列表项单击事件添加监听器
show.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener(){
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view,
int position, long id) {
//a.加载View.xml界面布局代表的视图
View viewDialog=getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.view, null);
//b.获得viewDialog中Id为image的组件
ImageView image=(ImageView)viewDialog.findViewById(R.id.image);
//c.设置image显示指定图片
image.setImageBitmap(BitmapFactory.decodeFile(fileNames.get(position)));
//d.使用对话框显示用户单击的图片
new AlertDialog.Builder(MediaProviderTest.this)
.setView(viewDialog).setPositiveButton("肯定", null)
.show();
}
});
//5.为add按钮的单击事件绑定监听器
addBtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//a.创建ContentValues对象,准备插入数据
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(Media.DISPLAY_NAME, "photo");
values.put(Media.DESCRIPTION, "示例图片");
values.put(Media.MIME_TYPE, "image/jpeg");
//b.插入数据,返回所插入数据对应的Uri
Uri uri = getContentResolver().insert(Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI, values);
//c.加载利用程序下photo图片
Bitmap bitmap=BitmapFactory.decodeResource(MediaProviderTest.this.getResources(),R.drawable.photo);
OutputStream os = null;
try{
os=getContentResolver().openOutputStream(uri);
bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, 100, os);
os.close();
}catch(IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
(2)主Activity布局文件/res/layout/main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/cat"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="查看所有图片"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/add"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="添加图片"/>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></ListView>
</LinearLayout>
(3)列表项布局/res/layout/line.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf⑻"?><LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/desc"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
(4)点击列表项,弹出对话框布局/res/layout/view.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf⑻"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/image"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
(5)效果演示
2、监听ContentProvider的数据改变
1.ContentObserver
(1)功能:帮助利用程序实现实时监听ContentProvider所同享的数据是不是改变,并随着ContentProvider的数据的改变而提供响。为了监听指定的ContentProvider的数据变化,我们通过ContentResolver向指定Uri注册ContentObserver监听器。
(2)重要方法
registerContentObserver(Uri uri,boolean notifyForDescendents,ContentObserver observer)
作用:向指定Uri注册ContentObserver监听器
参数:
uri:该监听器所监听的ContentProvider的Uri;
notifyForDescendents:设置为true,假定注册监听的Uri为content://abc,那末Uri为content://abc/xyz、content://abc/xyz/foo的数据改变时也会触发该监听器;若为false只有content://abc数据改变时才会触发该监听器;
2.开发思路
(1)通过ContentResolver向指定的Uri注册ContentObserver监听器(监听器类 SmsObserver),以便监听Uri对应的ContentProvider的数据变化;
getContentResolver().registerContentObserver(Uri.parse("content://sms"),true,new
SmsObserver(new Handler()));
其中,new SmsObserver(new Handler())为继承于ContentObserver子类对象,参数为Handler对象
(2)实现监听器类 SmsObserver。该监听器类 继承于ContentObserver类,并重写该基类所定义的onChange(boolean
selfChange)方法-----当它所监听的ContentProvider的数据产生改变时,该onChange将会被触发。
3.源码实例
package com.example.android_content_5;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.database.ContentObserver;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MonitorSms extends Activity {
private TextView sms;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
sms=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.message);
//1.为content://sms的数据改变注册监听器
getContentResolver().registerContentObserver(Uri.parse("content://sms"),true, new SmsObserver(new Handler()));
}
//2.提供自定义的ContentObserver监听器类
private final class SmsObserver extends ContentObserver
{
//a.构造方法
public SmsObserver(Handler handler)
{
super(handler);
}
public void onChange(boolean selfChange)
{
//b.查询发送箱中的短信(处于正在发送状态的信息放在发送箱),即查询content://sms/outbox的全部数据
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(Uri.parse("content://sms/outbox"), null, null, null, null);
while(cursor.moveToNext())
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//获得短信的发送地址
sb.append("address=").append(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("address")));
//获得短信的标题
sb.append(";subject=").append(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("subject")));
//获得短信的内容
sb.append(";body=").append(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("body")));
//获得短信的发送时间
sb.append(";time=").append(cursor.getLong(cursor.getColumnIndex("date")));
System.out.println("Has Sent SMS::"+sb.toString());
}
}
}
}
注释:Handler类
A Handler allows you to send and process Message and Runnable
objects associated with a thread's MessageQueue. Each Handler instance is associated with a single thread and that thread's message queue. When you create a new Handler, it is bound to the thread / message queue of the thread that is creating it -- from that
point on, it will deliver messages and runnables to that message queue and execute them as they come out of the message queue.
生活不易,码农辛苦
如果您觉得本网站对您的学习有所帮助,可以手机扫描二维码进行捐赠