背景:
最近公司由于项目需要,需要把web 的项目做成1个window 安装软件给到客户。我在网络上搜索了很多零零散散的教程,大多都不是很详细很全面。在此我进行总结成博文来分享出来,希望帮助到更多的人。
========project.iss end========
=======autoInstallJDK.bat begin==========
@echo off
echo ------begin----
:: 退到上级目录
cd ..
:: 获得jdk 的全路径,全路径=当前路径+jdk路径
:: "%~dp0" 这个是最起始的条用bat的cmd 的路径 所以我们要使用cd ..后退1个目录后用"%cd%" 来获得当前目录
echo "%~dp0"
echo "%cd%"
::设置jdkpath变量
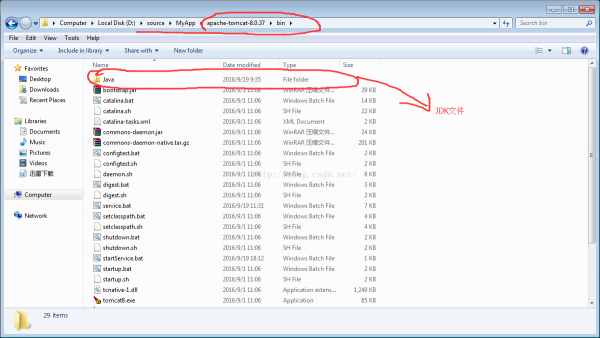
set jdkpath=%cd%\apache-tomcat⑻.0.37\bin\Java\jdk1.8.0_31
echo %jdkpath%
::setx variable value -m
:: setx 这个是用来设置环境变量的,并且会写入注册表. variable,会被覆盖,此操作不可逆的
:: variable 代表键 value代表值 -m代表写入系统环境变量,如果没有该参数会写入当前用户环境变量.
setx JAVA_HOME "%jdkpath%" -m
setx CLASSPATH ".;%%JAVA_HOME%%\lib\tools.jar;%%JAVA_HOME%%\lib\dt.jar" -m
echo %Path%
::追加path环境变量 find 后面/i代表疏忽大小写 &&履行成功履行的命令 ||履行失败履行的命令
echo %Path%|find /i "%java_home%" && set IsNull=true || set IsNull=false
echo %IsNull%
if not %IsNull%==true (
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path /t REG_SZ /d "%Path%;%%JAVA_HOME%%\bin;%%JAVA_HOME%%\jre\bin" /f
::设置当前用户环境变量
setx Path "%%JAVA_HOME%%\bin;%Path%"
)
exit
=======autoInstallJDK.bat end==========
======aotoInstallTomcat.bat==begin======
echo -------tomcat begin--------
::call 是用来调用另外一个批处理文件, install 是用来安装注册服务到windows的服务里面
call "%~dp0%service.bat" install tomcat8
echo -------tomcat install end------------------
::配置服务开机自启动
sc config tomcat8 start= auto
net start tomcat8
exit
======aotoInstallTomcat.bat==end======
MySql:官方下载地址:http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
版本号:mysql⑸.7.15-win32.zip
我在这里选择下载的是免安装的32位的绿色版本。
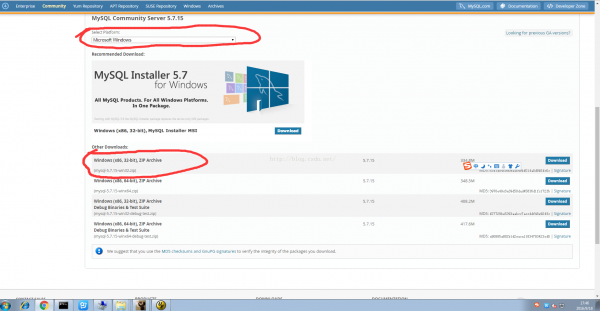
通过InnoSetup 工具生成的exe 的可安装文件,安装后我们发现,Mysql 的安装文件终究copy后的路径为:C:\Program Files\project\mysql⑸.7.15-win32
以下图所示:
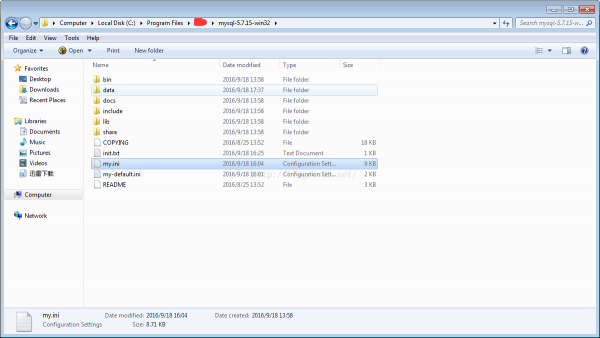
其中有1个my-default.ini 的文件,我在当前路径下面复制1份,然后在重新命名为my.ini
其中my.ini 中有1个必须要配置的项
#basedir这个路径是mysql 的安装路径
basedir="C:/Program Files/project/mysql⑸.7.15-win32"
#datadir 是数据库的根路径
datadir="C:/Program Files/project/mysql⑸.7.15-win32/data/"
以下为我的my.ini 的配置文件:
=================my.ini begin================
# MySQL Server Instance Configuration File
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Generated by the MySQL Server Instance Configuration Wizard
#
#
# Installation Instructions
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# On Linux you can copy this file to /etc/my.cnf to set global options,
# mysql-data-dir/my.cnf to set server-specific options
# (@localstatedir@ for this installation) or to
# ~/.my.cnf to set user-specific options.
#
# On Windows you should keep this file in the installation directory
# of your server (e.g. C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y). To
# make sure the server reads the config file use the startup option
# "--defaults-file".
#
# To run run the server from the command line, execute this in a
# command line shell, e.g.
# mysqld --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y\my.ini"
#
# To install the server as a Windows service manually, execute this in a
# command line shell, e.g.
# mysqld --install MySQLXY --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y\my.ini"
#
# And then execute this in a command line shell to start the server, e.g.
# net start MySQLXY
#
#
# Guildlines for editing this file
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# In this file, you can use all long options that the program supports.
# If you want to know the options a program supports, start the program
# with the "--help" option.
#
# More detailed information about the individual options can also be
# found in the manual.
#
#
# CLIENT SECTION
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# The following options will be read by MySQL client applications.
# Note that only client applications shipped by MySQL are guaranteed
# to read this section. If you want your own MySQL client program to
# honor these values, you need to specify it as an option during the
# MySQL client library initialization.
#
[client]
port=3306
[mysql]
default-character-set=utf8
# SERVER SECTION
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# The following options will be read by the MySQL Server. Make sure that
# you have installed the server correctly (see above) so it reads this
# file.
#
[mysqld]
# The TCP/IP Port the MySQL Server will listen on
port=3306
#Path to installation directory. All paths are usually resolved relative to this.
basedir="C:/Program Files/project/mysql⑸.7.15-win32"
#Path to the database root
datadir="C:/Program Files/project/mysql⑸.7.15-win32/Data/"
# The default character set that will be used when a new schema or table is
# created and no character set is defined
character-set-server=utf8
# The default storage engine that will be used when create new tables when
default-storage-engine=INNODB
# Set the SQL mode to strict
sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION"
# The maximum amount of concurrent sessions the MySQL server will
# allow. One of these connections will be reserved for a user with
# SUPER privileges to allow the administrator to login even if the
# connection limit has been reached.
max_connections=100
# Query cache is used to cache SELECT results and later return them
# without actual executing the same query once again. Having the query
# cache enabled may result in significant speed improvements, if your
# have a lot of identical queries and rarely changing tables. See the
# "Qcache_lowmem_prunes" status variable to check if the current value
# is high enough for your load.
# Note: In case your tables change very often or if your queries are
# textually different every time, the query cache may result in a
# slowdown instead of a performance improvement.
query_cache_size=32M
# The number of open tables for all threads. Increasing this value
# increases the number of file descriptors that mysqld requires.
# Therefore you have to make sure to set the amount of open files
# allowed to at least 4096 in the variable "open-files-limit" in
# section [mysqld_safe]
table_open_cache=256
# Maximum size for internal (in-memory) temporary tables. If a table
# grows larger than this value, it is automatically converted to disk
# based table This limitation is for a single table. There can be many
# of them.
tmp_table_size=35M
# How many threads we should keep in a cache for reuse. When a client
# disconnects, the client's threads are put in the cache if there aren't
# more than thread_cache_size threads from before. This greatly reduces
# the amount of thread creations needed if you have a lot of new
# connections. (Normally this doesn't give a notable performance
# improvement if you have a good thread implementation.)
thread_cache_size=8
#*** MyISAM Specific options
# The maximum size of the temporary file MySQL is allowed to use while
# recreating the index (during REPAIR, ALTER TABLE or LOAD DATA INFILE.
# If the file-size would be bigger than this, the index will be created
# through the key cache (which is slower).
myisam_max_sort_file_size=100G
# If the temporary file used for fast index creation would be bigger
# than using the key cache by the amount specified here, then prefer the
# key cache method. This is mainly used to force long character keys in
# large tables to use the slower key cache method to create the index.
myisam_sort_buffer_size=69M
# Size of the Key Buffer, used to cache index blocks for MyISAM tables.
# Do not set it larger than 30% of your available memory, as some memory
# is also required by the OS to cache rows. Even if you're not using
# MyISAM tables, you should still set it to 8⑹4M as it will also be
# used for internal temporary disk tables.
key_buffer_size=50M
# Size of the buffer used for doing full table scans of MyISAM tables.
# Allocated per thread, if a full scan is needed.
read_buffer_size=64K
read_rnd_buffer_size=256K
# This buffer is allocated when MySQL needs to rebuild the index in
# REPAIR, OPTIMZE, ALTER table statements as well as in LOAD DATA INFILE
# into an empty table. It is allocated per thread so be careful with
# large settings.
sort_buffer_size=256K
#*** INNODB Specific options ***
# Use this option if you have a MySQL server with InnoDB support enabled
# but you do not plan to use it. This will save memory and disk space
# and speed up some things.
#skip-innodb
# Additional memory pool that is used by InnoDB to store metadata
# information. If InnoDB requires more memory for this purpose it will
# start to allocate it from the OS. As this is fast enough on most
# recent operating systems, you normally do not need to change this
# value. SHOW INNODB STATUS will display the current amount used.
#innodb_additional_mem_pool_size=14M
# If set to 1, InnoDB will flush (fsync) the transaction logs to the
# disk at each commit, which offers full ACID behavior. If you are
# willing to compromise this safety, and you are running small
# transactions, you may set this to 0 or 2 to reduce disk I/O to the
# logs. Value 0 means that the log is only written to the log file and
# the log file flushed to disk approximately once per second. Value 2
# means the log is written to the log file at each commit, but the log
# file is only flushed to disk approximately once per second.
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1
# The size of the buffer InnoDB uses for buffering log data. As soon as
# it is full, InnoDB will have to flush it to disk. As it is flushed
# once per second anyway, it does not make sense to have it very large
# (even with long transactions).
innodb_log_buffer_size=1M
# InnoDB, unlike MyISAM, uses a buffer pool to cache both indexes and
# row data. The bigger you set this the less disk I/O is needed to
# access data in tables. On a dedicated database server you may set this
# parameter up to 80% of the machine physical memory size. Do not set it
# too large, though, because competition of the physical memory may
# cause paging in the operating system. Note that on 32bit systems you
# might be limited to 2⑶.5G of user level memory per process, so do not
# set it too high.
innodb_buffer_pool_size=96M
# Size of each log file in a log group. You should set the combined size
# of log files to about 25%⑴00% of your buffer pool size to avoid
# unneeded buffer pool flush activity on log file overwrite. However,
# note that a larger logfile size will increase the time needed for the
# recovery process.
innodb_log_file_size=20M
# Number of threads allowed inside the InnoDB kernel. The optimal value
# depends highly on the application, hardware as well as the OS
# scheduler properties. A too high value may lead to thread thrashing.
innodb_thread_concurrency=18
=================my.ini end=================
在当前mysql的目录下面创建data的空文件夹
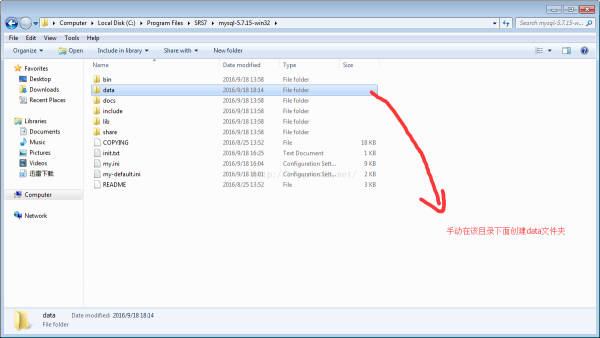
创建mysql 的批处理脚本:
我命名为:mysql_init.bat
在写mysql_init.bat文件之前,我们先手动通过cmd 的命令来配置mysql,然后在把相干命写入到批处理文件中来。
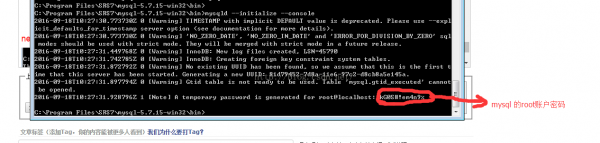
mysqld --initialize 使用这个指令进行初始化的进程中我没有看不到mysql root 账户的初始密码和安装日志信息
mysqld --initialize --console 其中--console 的意思是安装信息打印到控制台
履行后的打印信息以下图所示:
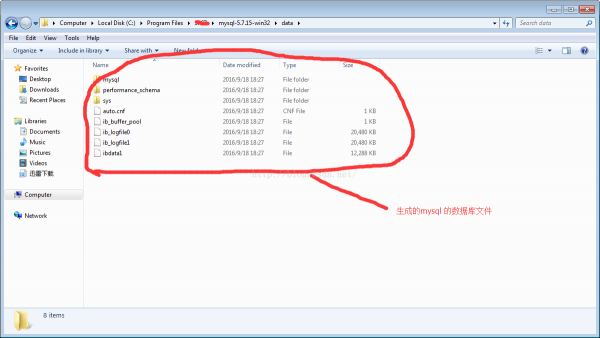
履行完成后会在mysql 的安装路径下面data文件夹下会生成相干的数据库文件。
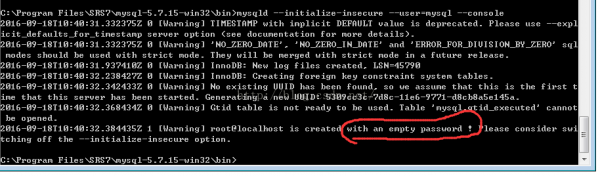
mysqld --initialize-insecure --user=mysql --console 初始化不会生成密码
mysqld install mysql --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\SRS7\mysql⑸.7.15-win32\my.ini"
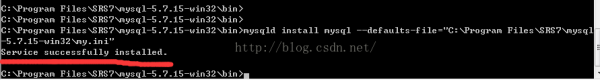
这个时候在window的服务列表里面就会多1个mysql 的服务
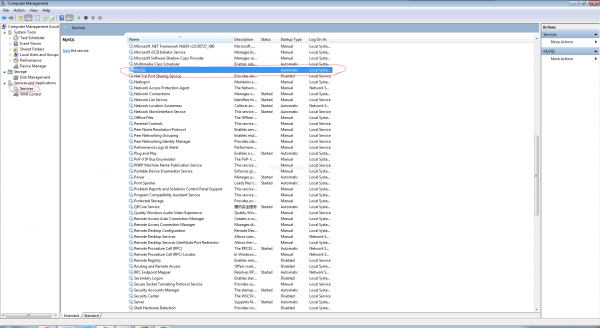
net start mysql
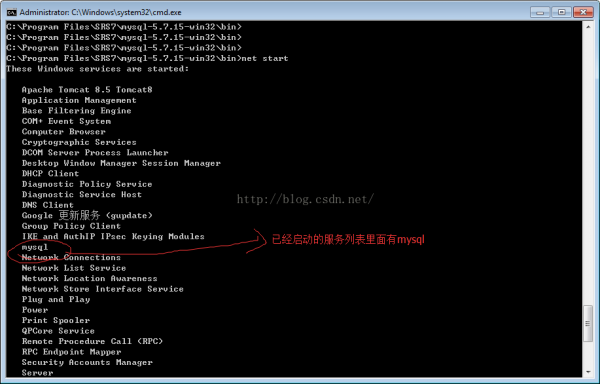
通过指令:net start 可以查看window已启动的服务有哪1些
mysqladmin -u root -p password root
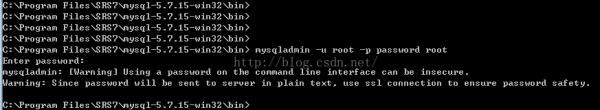
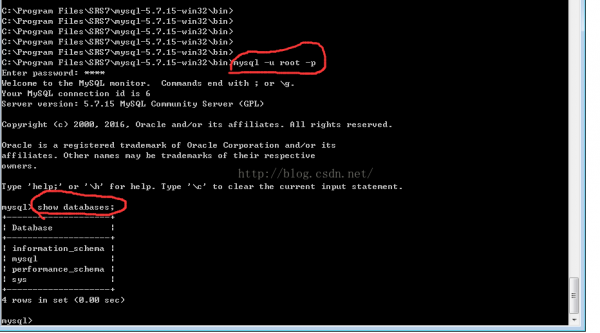
登录数据库:
mysql -u root -p
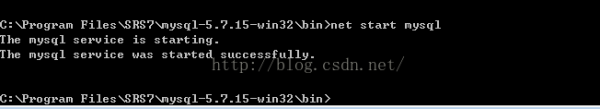
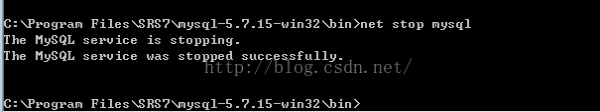
net stop mysql
停止mysql 的服务
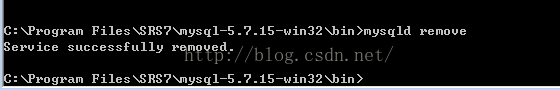
mysqld remove 删除注册到window的mysql服务
mysql_init.bat内容以下:
=============begin==================
cd /d %~dp0
"%cd%\mysqld.exe" --initialize-insecure --user=mysql --console
echo -----mysql init succee-----
pause;
mysqld install mysql --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\SRS7\mysql⑸.7.15-win32\my.ini
echo -----mysql service install succee-----
pause;
net start mysql
sc config mysql start=auto
net stop mysql
net start mysql
echo 安装终了
pause;
"%cd%\mysqladmin" -u root password root
echo 修改密码终了
pause;
cd ..
"%cd%\bin\mysql.exe" -uroot -proot < "%cd%\SqlFile\foodserver.sql"
echo 建表终了
pause;
echo 建立新用户终了
=============end===================
可能遇到问题汇总:
1.首次履行exe文件进行安装的时候发现tomcat8 的服务,已注册到windows的系统服务里面,但是启动失败了
通过tomcat/logs/下面可以查看失败的缘由。
这个是大概配置的教程,算是很全面了,希望帮助到更多的人。
如果大家有疑问可以提出共同交换:QQ:156149728
