线段树
来源:程序员人生 发布时间:2015-06-17 09:08:45 阅读次数:3753次
线段树简介:
线段树的定义以下:
1棵2叉树,记为T (a,b),参数a,b表示该结点表示区间[a,b]。区间的长度b-a记为L。递归定义T[a,b]:
若L>1 :[a, (a+b) div 2]为 T的左儿子
[(a+b)div 2,b]为T的右儿子。
若L=1 :T为1个叶子结点。
表示区间[1, 10]的线段树表示以下:
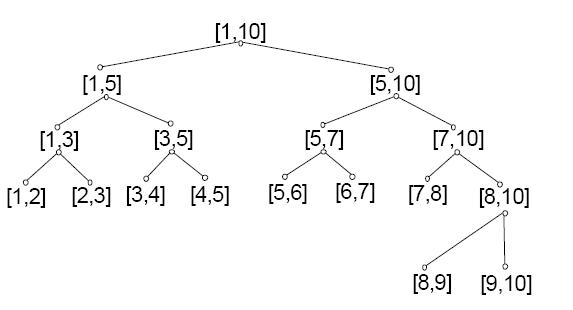
树1般有两种情势:1、以点为结点。2、以线段为结点。区分如图:上面1个以线段为结点,下面1个以点为结点:
对线段树存在:
定理:线段树把区间上的任意1条线段都分成不超过2logL条线段。
这个结论为线段树能在O(logL)的时间内完成1条线段的插入、删除、查找等工作,提供了理论根据。
对线段树的可以进行扩大。
1. 测度。结点所表示区间中线段覆盖过的长度,存储在各结点中。
2. 独立线段数。区间中互不相交的线段条数。
3. 权和。区间所有元线段的权和。
测度的递推公式以下:
a[j] - a[i] 该结点 Count>0
M = 0 该结点为叶结点且 Count=0
Leftchild ↑ .M + Rightchild ↑ .M 该结点为内部结点且 Count=0连续段数
这里的连续段数指的是区间的并可以分解为多少个独立的区间。如 [1 , 2] ∪[2,3]∪ [5 , 6] 可以分解为两个区间[1 , 3] 与 [5 , 6] ,则连续段数为 2 。增加1个数据域 Lines_Tree.line 表示该结点的连续段数。 Line 的讨论比较复杂,内部结点不能简单地将左右孩子的 Line 相加。所以再增加 Lines_Tree.lbd 与 Lines_Tree.rbd 域。定义以下:
1 左端点 I 被描写区间盖到
lbd =
0 左端点 I 不被描写区间盖到
1 右端点 J 被描写区间盖到
rbd =
0 右端点 J 不被描写区间盖到
lbd 与 rbd 的实现:
1 该结点 count > 0
lbd = 0 该结点是叶结点且 count = 0
leftchild ↑ .lbd 该结点是内部结点且 Count=0
1 该结点 count > 0
rbd = 0 该结点是叶结点且 count = 0
rightchild ↑ .rbd 该结点是内部结点且 Count=0
有了 lbd 与 rbd , Line 域就能够定义了:
1 该结点 count > 0
Line = 0 该结点是叶结点且 count =0
Leftchild ↑ .Line + Rightchild ↑.Line - 1 当该结点是内部结点且 Count=0 , Leftchild ↑ .rbd = 1 且 Rightchild ↑ .lbd = 1
Leftchild ↑.Line + Rightchild ↑ .Line 当该结点是内部结点且 Count=0 , Leftchild ↑ .rbd 与 Rightchild ↑ .lbd 不都为1
6.2 利用线段树实现区间的动态插入和删除
6.2.1 实例
PKU JudgeOnline, 1151, Atlantis.
6.2.2 问题描写
在2维平面分部着1些矩形,矩形有可能重合。求矩形的总面积。
6.2.3 分析
这个题在《算法艺术与信息学比赛》中第1章介绍数据结构时,讲到线段树的时候有解题分析。
用线段树来记载纵向上是否是被覆盖,用测度来表示区间中被覆盖了多少长度。
为了下降复杂度,可以将坐标离散化,以下图所示:
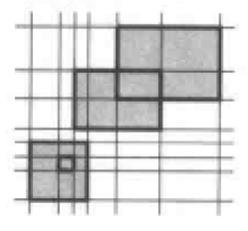
从左到右扫描长方形的左边边和右边边,如果是左边边则加入线段树中,否则从线段书中删除。同时用横向扫描的距离乘以线段树的测度,就得到了扫描过了的被覆盖的面积。
本题和PKU JudgeOnline,1117, Picture题都对线段树进行了扩大。本题只用到了测度的扩大,而1117题还用到了独立线段数的扩大。
//离散化+ 线段树+ 扫描线
//本题与JudgeOnline 1177 picture 极类似,现在回想起来乃至比1177 还要简单1些.与1177 不同的是本题中的坐标是浮点
//类型的故不能将坐标直接离散.我们必须为它们建立1个对应关系,用1个整数去对应1个浮点数
//这样的对应关系在本题的数组y[] 中
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int st, ed,c; //c : 区间被覆盖的层数,m: 区间的测度
double m;
}ST[802];
struct line{
doublex,y1,y2; //纵方向直线, x:直线横坐标, y1 y2:直线上的下面与上面的两个纵坐标
bools; //s = 1: 直线为矩形的左侧, s = 0:直线为矩形的右侧
}Line[205];
double y[205],ty[205]; //y[] 整数与浮点数的对应数组;ty[]:用来求y[]的辅助数组
void build(int root, int st, int ed){
ST[root].st = st;
ST[root].ed = ed;
ST[root].c = 0;
ST[root].m = 0;
if(ed - st> 1){
int mid= (st+ed)/2;
build(root*2, st, mid);
build(root*2+1, mid, ed);
}
}
inline void updata(int root){
if(ST[root].c> 0)
//将线段树上区间的端点分别映照到y[]数组所对应的浮点数上,由此计算出测度
ST[root].m = y[ST[root].ed⑴] -y[ST[root].st⑴];
else if(ST[root].ed - ST[root].st == 1)
ST[root].m = 0;
elseST[root].m = ST[root*2].m + ST[root*2+1].m;
}
void insert(int root, int st, int ed){
if(st <=ST[root].st && ST[root].ed <= ed){
ST[root].c++;
updata(root);
return;
}
if(ST[root].ed- ST[root].st == 1)return ;//不出错的话这句话就是冗余的
int mid =(ST[root].ed + ST[root].st)/2;
if(st <mid)
insert(root*2, st, ed);
if(ed >mid)
insert(root*2+1, st, ed);
updata(root);
}
void Delete(int root, int st, int ed){
if(st <=ST[root].st && ST[root].ed <= ed){
ST[root].c--;
updata(root);
return;
}
if(ST[root].ed- ST[root].st == 1)return ; //不出错的话这句话就是冗余的
int mid =(ST[root].st + ST[root].ed)/2;
if(st <mid)
Delete(root*2, st, ed);
if(ed >mid)
Delete(root*2+1, st, ed);
updata(root);
}
int Correspond(int n, double t){
//2分查找出浮点数t 在数组y[]中的位置(此即所谓的映照关系)
intlow,high,mid;
low = 0; high = n⑴;
while(low< high){
mid = (low+high)/2;
if(t> y[mid])
low = mid + 1;
elsehigh = mid;
}
returnhigh+1;
}
bool cmp(line l1, line l2){
return l1.x< l2.x;
}
int main()
{
intn,i,num,l,r,c=0;
doublearea,x1,x2,y1,y2;
while(cin>>n,n){
for(i =0; i < n; i++){
cin>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
Line[2*i].x = x1; Line[2*i].y1 =y1; Line[2*i].y2 = y2; Line[2*i].s = 1;
Line[2*i+1].x = x2; Line[2*i+1].y1= y1; Line[2*i+1].y2 = y2; Line[2*i+1].s = 0;
ty[2*i] = y1; ty[2*i+1] = y2;
}
n <<= 1;
sort(Line, Line+n, cmp);
sort(ty, ty+n);
y[0] = ty[0];
//处理数组ty[]使之不含重覆元素,得到新的数组寄存到数组y[]中
for(i=num=1;i < n; i++)
if(ty[i]!= ty[i⑴])
y[num++] = ty[i];
build(1, 1, num); //树的叶子结点与数组y[]中的元素个数相同,以便建立逐一对应的关系
area = 0;
for(i =0; i < n⑴; i++){
//由对应关系计算出线段两端在树中的位置
l = Correspond(num, Line[i].y1);
r = Correspond(num, Line[i].y2);
if(Line[i].s)//插入矩形的左侧
insert(1, l, r);
else //删除矩形的右侧
Delete(1, l, r);
area += ST[1].m * (Line[i+1].x -Line[i].x);
}
cout<<"Testcase #"<<++c<<endl<<"Totalexplored area: ";
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<area<<endl<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
计算数组区间第K大的数
PKU JudgeOnline, 2761, Feed the dogs则是线段树的另外1个利用:实用线段树来计算数组区间[i, j]中元素第k小(或第K大)的数。只要添写1个函数,根据线段树中每一个结点的覆盖树木来判断第k大的树是哪个。
当初始化,或区间[i, j]产生变化时,需要对线段树进行添加或删除操作。每当增加(或删除)1个大小为X的点时,就在树上添加(或删除)1条(X,MaxLen)的线段(不含端点),当要查询1个点的排名时,只要看看其上有多少条线段就能够了。
int query(int root, intcount)
{
if(count<= ST[root].c){
returnST[root].st;
}else if(ST[root].ed - ST[root].st == 1){
returnST[root].ed;
}
count -= ST[root].c;
if(count<= ST[root*2+1].c){
returnquery(root*2, count);
}else{
returnquery(root*2+1, count);
}
}
生活不易,码农辛苦
如果您觉得本网站对您的学习有所帮助,可以手机扫描二维码进行捐赠





