Varnish是1款高性能的开源HTTP加速器,挪威最大的在线报纸 Verdens Gang (http://www.vg.no) 使用3台Varnish代替了原来的12台squid,性能竟然比之前更好。
Varnish 的作者Poul-Henning Kamp是FreeBSD的内核开发者之1,他认为现在的计算机比起1975年已复杂许多。在1975年时,贮存媒介只有两种:内存与硬盘。但现在计算 机系统的内存除主存外,还包括了cpu内的L1、L2,乃至有L3快取。硬盘上也有自己的快取装置,因此squid cache自行处理物件替换的架构不可能得知这些情况而做到最好化,但操作系统可以得知这些情况,所以这部分的工作应当交给操作系统处理,这就是 Varnish cache设计架构。
【以上摘自http://www.oschina.net/p/varnish】
空话说完了,接下来就是怎样使用它了。本文描写的内容基于Varnish 4.1.2版本。
(1)源码安装
下面这个是Varnish的官网:https://www.varnish-cache.org/
github的地址:https://github.com/varnishcache/varnish-cache
下载下来源码包,进行编译安装。
(2)命令安装
在官网上可以看到说明:
https://www.varnish-cache.org/releases/install_ubuntu.html#install-ubuntu
apt-get install apt-transport-https
curl https://repo.varnish-cache.org/GPG-key.txt | apt-key add -
echo "deb https://repo.varnish-cache.org/ubuntu/ trusty varnish⑷.1" \
>> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/varnish-cache.list
apt-get update
apt-get install varnish可以看到,通过命令行直接安装比较方便。
这1点还是值得注意的,我在配置的时候,发现网上大部份文档都是之前的版本,但是在4.x版本以后,配置方式产生了变化,也折腾了些时间,所以,希望能帮助你跳过坑。
默许的端口是监听6081,你怎样知道?
看这个文件:
vi /etc/default/varnishtfxiaozi@server:~$ cat /etc/default/varnish
# Configuration file for Varnish Cache.
#
# /etc/init.d/varnish expects the variables $DAEMON_OPTS, $NFILES and $MEMLOCK
# to be set from this shell script fragment.
#
# Note: If systemd is installed, this file is obsolete and ignored. You will
# need to copy /lib/systemd/system/varnish.service to /etc/systemd/system/ and
# edit that file.
# Should we start varnishd at boot? Set to "no" to disable.
START=yes
# Maximum number of open files (for ulimit -n)
NFILES=131072
# Maximum locked memory size (for ulimit -l)
# Used for locking the shared memory log in memory. If you increase log size,
# you need to increase this number as well
MEMLOCK=82000
DAEMON_OPTS="-a :6081 \
-T localhost:6082 \
-f /etc/varnish/default.vcl \
-S /etc/varnish/secret \
-s malloc,24G"
tfxiaozi@server:~$ 没错啦,就是这里,Varnish运行时占用了6081端口,6082用作管理。
-a 如果希望使用80端口直接访问,修改成80便可
-s 使用的内存大小
-S 认证的密钥文件 varnishadm -T localhost:6082 -S secret
-f 指定了Varnish运行起来时需要加载的配置文件,用来管理后端服务器在上面的配置中可以看到,密钥文件在/etc/varnish下。
访问http://varnish_VPS_public_IP:6081,前面是Varnish安装的机器ip,此时会出现503访问毛病,缘由是没有配置后端要cache的服务器。
这里以后端FastDFS存储集群机器为例进行配置,目的是让Varnish对FastDFS的Storage节点进行缓存,以下降直接访问Storage节点酿成的压力。
Storage1: 10.10.10.81;
Storage2: 10.10.10.82.
给出详细的配置文件:
root@server:/etc/varnish# cat default.vcl
#
# This is an example VCL file for Varnish.
#
# It does not do anything by default, delegating control to the
# builtin VCL. The builtin VCL is called when there is no explicit
# return statement.
#
# See the VCL chapters in the Users Guide at https://www.varnish-cache.org/docs/
# and https://www.varnish-cache.org/trac/wiki/VCLExamples for more examples.
# Marker to tell the VCL compiler that this VCL has been adapted to the
# new 4.0 format.
vcl 4.0;
import std;
import directors;
# Default backend definition. Set this to point to your content server.
#backend default {
# .host = "127.0.0.1";
# .port = "8080";
#}
#probe healthcheck {
# .url = "/";
# .interval = 6s;
# .timeout = 1s;
# .window = 5;
# .threshold = 3;
#}
backend fdfs_g1_s1 {
.host = "10.10.10.81";
.port = "10000";
# .probe = healthcheck; #健康状态检测
}
backend fdfs_g1_s2 {
.host = "10.10.10.82";
.port = "10000";
# .probe = healthcheck; #健康状态检测
}
acl purgers {
"localhost";
"127.0.0.1";
}
sub vcl_init {
new vdir = directors.round_robin();
vdir.add_backend(fdfs_g1_s1);
vdir.add_backend(fdfs_g1_s2);
return (ok);
}
sub vcl_recv {
# Happens before we check if we have this in cache already.
#
# Typically you clean up the request here, removing cookies you don't need,
# rewriting the request, etc.
set req.backend_hint = vdir.backend();
if (req.http.x-forwarded-for) {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = req.http.X-Forwarded-For + ", " + client.ip;
} else {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip;
}
if (req.method == "PURGE") { # PURGE要求的处理
if (!client.ip ~ purgers) {
return(synth(405,"Method not allowed"));
}
#清算缓存
return (purge);
}
# 制止缓存的文件
if (req.url ~ "\.(php|jsp|do)($|\?|#)") {
return (pass);
}
if (req.method == "PRI") {
#/* We do not support SPDY or HTTP/2.0 */
return (synth(405));
}
if (req.method != "GET" &&
req.method != "HEAD" &&
req.method != "PUT" &&
req.method != "POST" &&
req.method != "TRACE" &&
req.method != "OPTIONS" &&
req.method != "DELETE") {
#/* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird. */
return (pipe);
}
if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD") {
#/* We only deal with GET and HEAD by default */
return (pass);
}
if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie) {
#/* Not cacheable by default */
return (pass);
}
return (hash);
}
sub vcl_backend_response {
# Happens after we have read the response headers from the backend.
#
# Here you clean the response headers, removing silly Set-Cookie headers
# and other mistakes your backend does.
if (bereq.url ~ "^[^?]*\.(7z|avi|bmp|bz2|css|csv|doc|docx|eot|flac|flv|gif|gz|ico|jpeg|jpg|js|less|mka|mkv|mov|mp3|mp4|mpeg|mpg|odt|otf|ogg|ogm|opus|pdf|png|ppt|pptx|rar|rtf|svg|svgz|swf|tar|tbz|tgz|ttf|txt|txz|wav|webm|webp|woff|woff2|xls|xlsx|xml|xz|zip)(\?.*)?$") {
unset beresp.http.set-cookie;
}
# Large static files are delivered directly to the end-user without
# waiting for Varnish to fully read the file first.
# Varnish 4 fully supports Streaming, so use streaming here to avoid locking.
if (bereq.url ~ "^[^?]*\.(7z|avi|bz2|flac|flv|gz|mka|mkv|mov|mp3|mp4|mpeg|mpg|ogg|ogm|opus|rar|tar|tgz|tbz|txz|wav|webm|xz|zip)(\?.*)?$") {
unset beresp.http.set-cookie;
set beresp.do_stream = true; # Check memory usage it'll grow in fetch_chunksize blocks (128k by default) if the backend doesn't send a Content-Length header, so only enable it for big objects
set beresp.do_gzip = false; # Don't try to compress it for storage
}
# Set 2min cache if unset for static files
if (beresp.ttl <= 0s || beresp.http.Set-Cookie || beresp.http.Vary == "*") {
set beresp.ttl = 120s; # Important, you shouldn't rely on this, SET YOUR HEADERS in the backend
set beresp.uncacheable = true;
return (deliver);
}
# Allow stale content, in case the backend goes down.
# make Varnish keep all objects for 6 hours beyond their TTL
set beresp.grace = 6h;
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_backend_fetch {
return (fetch);
}
sub vcl_pipe {
# By default Connection: close is set on all piped requests, to stop
# connection reuse from sending future requests directly to the
# (potentially) wrong backend. If you do want this to happen, you can undo
# it here.
# unset bereq.http.connection;
return (pipe);
}
sub vcl_pass {
return (fetch);
}
sub vcl_hash {
hash_data(req.url);
if (req.http.host) {
hash_data(req.http.host);
} else {
hash_data(server.ip);
}
return (lookup);
}
sub vcl_purge {
return (synth(200, "Purged"));
}
sub vcl_hit {
if (obj.ttl >= 0s) {
#// A pure unadultered hit, deliver it
return (deliver);
}
if (obj.ttl + obj.grace > 0s) {
#// Object is in grace, deliver it
#// Automatically triggers a background fetch
return (deliver);
}
#// fetch & deliver once we get the result
return (miss);
}
sub vcl_miss {
return (fetch);
}
sub vcl_deliver {
set resp.http.x-hits = obj.hits;
if (obj.hits > 0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "Hit varnish cache";
}else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "Miss varnish cache";
}
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_synth {
set resp.http.Content-Type = "text/html; charset=utf⑻";
set resp.http.Retry-After = "5";
synthetic( {"<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>"} + resp.status + " " + resp.reason + {"</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Error "} + resp.status + " " + resp.reason + {"</h1>
<p>"} + resp.reason + {"</p>
<h3>Guru Meditation:</h3>
<p>XID: "} + req.xid + {"</p>
<hr>
<p>Varnish cache server</p>
</body>
</html>
"} );
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_backend_error {
set beresp.http.Content-Type = "text/html; charset=utf⑻";
set beresp.http.Retry-After = "5";
synthetic( {"<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>"} + beresp.status + " " + beresp.reason + {"</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Error "} + beresp.status + " " + beresp.reason + {"</h1>
<p>"} + beresp.reason + {"</p>
<h3>Guru Meditation:</h3>
<p>XID: "} + bereq.xid + {"</p>
<hr>
<p>Varnish cache server</p>
</body>
</html>
"} );
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_fini {
return (ok);
}默许情况下,如果只有1台机器做web server,使用backend default进行配置便可。如果是多台机器提供相同的内容服务,那末可以将多个web server进行组管理,通过robin轮询或random提供服务,具体要注意的细节:
①自定义后台server
backend fdfs_g1_s1 {
.host = "10.10.10.81";
.port = "10000";
# .probe = healthcheck; #健康状态检测
}
backend fdfs_g1_s2 {
.host = "10.10.10.82";
.port = "10000";
# .probe = healthcheck; #健康状态检测
}②初始化
sub vcl_init {
new vdir = directors.round_robin();
vdir.add_backend(fdfs_g1_s1);
vdir.add_backend(fdfs_g1_s2);
return (ok);
}初始化操作放到init中便可。
③然后,需要在vcl_recv中进行设置当前使用的backend,
set req.backend_hint = vdir.backend();做完这3步,varnish就配置好了,固然还可以根据需要配置节点健康检查。
履行以下命令:
service varnish start可以通过netstat -unltp | grep varnish 查看当前端口是不是被varnish占用:
root@server:/etc/varnish# netstat -unltp | grep varnish
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6081 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 26565/varnishd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6082 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 26565/varnishd
tcp6 0 0 :::6081 :::* LISTEN 26565/varnishd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:6082 :::* LISTEN 26565/varnishd 既然配置好了,那末就改测试1下,看看效果怎样样了。
Storage1: 10.10.10.81;
Storage2: 10.10.10.82;
我这里varnish装在192.168.165.21机器上,配置了双网卡。
可以看到,当访问6081端口时,出现了nginx的界面,这是由于在FastDFS配置了Storage使用Nginx提供http服务,也就是说当前配置到后端服务器是OK了。
下面来测试1下缓存到底有无起作用?
第1次:
Request URL:http://192.168.165.21:6081/group1/M00/00/00/CgoK0ldybhOAYFAfAAAOelbujmQ479.png
Request Method:GET
Status Code:200 OK
Remote Address:192.168.165.21:6081
Response Headers
view source
Accept-Ranges:bytes
Age:0
Connection:keep-alive
Content-Length:3706
Content-Type:image/png
Date:Tue, 28 Jun 2016 12:31:56 GMT
Last-Modified:Tue, 28 Jun 2016 12:31:15 GMT
Server:nginx/1.8.1
Via:1.1 varnish-v4
X-Cache:Miss varnish cache
x-hits:0
X-Varnish:98311
Request Headers
view source
Accept:text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Encoding:gzip, deflate, sdch
Accept-Language:zh-CN,zh;q=0.8
Connection:keep-alive
DNT:1
Host:192.168.165.21:6081
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests:1
User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/48.0.2564.109 Safari/537.36可以看到,第1次没有再缓存中命中:X-Cache:Miss varnish cache
第2次:
Request URL:http://192.168.165.21:6081/group1/M00/00/00/CgoK0ldybhOAYFAfAAAOelbujmQ479.png
Request Method:GET
Status Code:200 OK
Remote Address:192.168.165.21:6081
Response Headers
view source
Accept-Ranges:bytes
Age:16
Connection:keep-alive
Content-Length:3706
Content-Type:image/png
Date:Tue, 28 Jun 2016 12:31:56 GMT
Last-Modified:Tue, 28 Jun 2016 12:31:15 GMT
Server:nginx/1.8.1
Via:1.1 varnish-v4
X-Cache:Hit varnish cache
x-hits:1
X-Varnish:13 98312
Request Headers
view source
Accept:text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Encoding:gzip, deflate, sdch
Accept-Language:zh-CN,zh;q=0.8
Cache-Control:max-age=0
Connection:keep-alive
DNT:1
Host:192.168.165.21:6081
If-Modified-Since:Tue, 28 Jun 2016 12:31:15 GMT
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests:1
User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/48.0.2564.109 Safari/537.36可以看到,第2次命中:X-Cache:Hit varnish cache。
配置文件指定了PURGE和IP 就能够用curl 清算缓存
root@server:/etc/varnish# curl -X PURGE http://127.0.0.1:6081/group1/M00/00/00/CgoK0ldybhOAYFAfAAAOelbujmQ479.png
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>200 Purged</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Error 200 Purged</h1>
<p>Purged</p>
<h3>Guru Meditation:</h3>
<p>XID: 98320</p>
<hr>
<p>Varnish cache server</p>
</body>
</html>
root@server:/etc/varnish# ①varnishstat
可以查看缓存命中率
缓存命中率的高低,直接反应Varnish的运行状态,以下通过varnishstat命令查看状态信息:
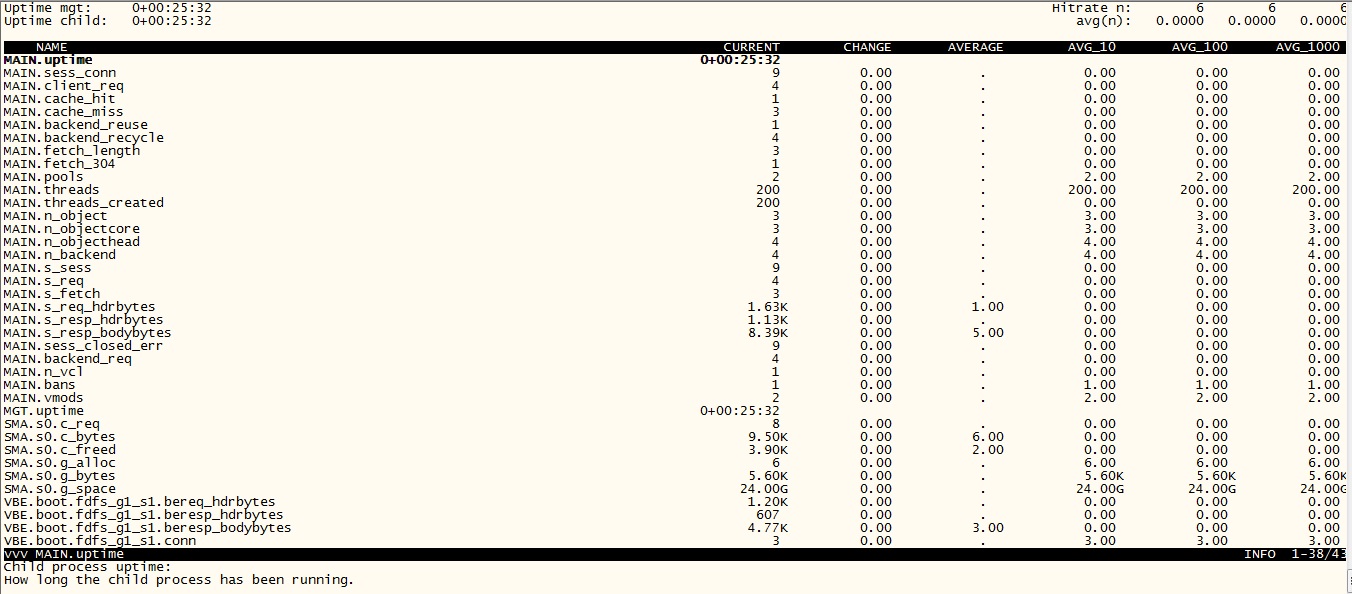
Hitrate n 第1个数字范围0⑴0,第2个数字范围0⑴00,第3个数字范围0⑴000。分别表示过去N秒内的
avg(n) 里的内容是命中率,需要乘以100转换成百分比。
②varnishlog
可以查看实光阴志。
1篇英文文档
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-configure-varnish-cache⑷-0-with-ssl-termination-on-ubuntu⑴4-04
github上1篇关于4.0的详细配置模板:
https://github.com/mattiasgeniar/varnish⑷.0-configuration-templates/blob/master/default.vcl
1篇关于之前低版本的配置,里面讲了关于Varnish性能优化和varnishadm 命令。
http://xiaodong88.blog.51cto.com/1492564/1304988
