hibernate作为orm模型的实现的1种,是java的对象模型和关系模型之间的桥梁,主要通过jdbc
的封装来到达操作数据库的目的,提供了1套相对全面的自动化的api。简单摹拟1下hibernate的
运行原理,其实主要还是jdbc的使用,还是直接看看这个小例子
package com.tgb.cfl.hibernate;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 摹拟hibernatesession接口
* @author 陈方林
*
*
*/
public class Session {
//寄存实体属性
private Map<String ,String > columns = new HashMap<String ,String >();
//字符串数组寄存实体的get方法集合
String methodNames[];
//初始化实体类属性和方法集合
public Session () {
//初始化实体,这里就不用读取配置文件的方式了,有点麻烦。
columns.put("name", "name");
columns.put("age", "age");
methodNames = new String[columns.size()];
}
/**
* save方法,持久化对象
* @param user
*/
public void save(Person person) {
//strColumn代表
数据库中表中的属性列。并将其连接起来。
String strColumn = "";
int index=0;
for(String key :columns.keySet())
{
strColumn +=key+",";
String v = columns.get(key);
//取得属性的get方法
v = "get" + Character.toUpperCase(v.charAt(0)) + v.substring(1);
methodNames[index] = v;
index++;
}
strColumn = strColumn.substring(0, strColumn.length()⑴);
//拼接参数占位符,即:(?, ?)
String strValue = "";
for(int i=0;i<columns.size();i++)
strValue +="?,";
//获得字符串子串
strValue = strValue.substring(0,strValue.length()⑴);
String sql = "insert into " + "Person" +"(" + strColumn + ")" + " values (" + strValue + ")";
System.out.println(sql);
try {
//获得连接
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/test" ,"root", "123456");
//jdbcstate对象
PreparedStatement state = (PreparedStatement) con.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i=0;i<methodNames.length;i++) {
//利用反射得到每个方法的对象
Method method = person.getClass().getMethod(methodNames[i]);
//得到他的返回类型
Class cla = method.getReturnType();
//根据返回类型来设置插入
数据库中的每一个属性值。
if(cla.getName().equals("java.lang.String")) {
String returnValue = (String)method.invoke(person);
state.setString(i+1, returnValue);
}
else if(cla.getName().equals("int")) {
Integer returnValue = (Integer) method.invoke(person);
state.setInt(i+1, returnValue);
}
}
//履行更新
state.executeUpdate();
state.close();
con.close();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.setAge("1");
p.setName("s2");
Session session = new Session();
try {
session.save(p);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这个例子主要还是摹拟session接口中对实体类的操作,主要分为这样几个步骤
1.动态拼接sql语句
2.根据反射得到实体类属性的操作方法get***
3.得到数据库连接
4.通过PreparedStatement对象来更新数据
这个是jdbc的对象,步骤主要又分为
a)从connection中获得PreparedStatement对象
b)利用PreparedStatement对象配合get方法得到属性值
5.垃圾回收(回收连接,对象关闭)
我们通过这个例子再回头看看hibernate,hibernate给我们做了甚么?
第1步:动态拼接sql语句是怎样实现的呢?hibernate中有这样1个配置文件叫***.hbm.xml,用来配置实体和数据库之间的关系。这个也是hibernate约定好的,你这样写了,最后就会读取这样后缀名的文件这个是第1步。
第2步:利用反射得到对应的get方法这个是利用反射来做到的主要还是通过jdk内部的这个
java.util.reflect.method这个类来做的。也是在jdk的api基础上做的。
第3步:得到数据库连接。hibernate中有这样1个配置文件叫做hibernate.properties配置文件,内部配置了数据库连接方言,数据库驱动,数据库地址,用户名密码等等。
例如:
也是hibernate这样来约定的,好了你程序中在指定文件夹有这个文件,我直接读取节点的数据便可。只不过上面的例子是在代码里面写死了。
第4步:这个是jdbc的preparedstatement对象的api
第5步:对应的是jdk的api。
标准的hibernate步骤以下:
1.通过Configuration().configure();读取并解析hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件
2.读取hibernate.cfg.xml//读取并解析映照信息
3.通过config.buildSessionFactory();//创建SessionFactory
4.sessionFactory.openSession();//打开Sesssion
5.session.beginTransaction();//创建事务Transation
6.persistent operate持久化操作
7.session.getTransaction().commit();//提交事务
8.关闭Session、SesstionFactory
再通过这张图,我们发现其实hibernate也就是在JDBC上面多加了1层。让我想起之前哪里听到1句话,灵活配置
是甚么?不过就是加1层,颇具喜感,后来1想却又几分道理。
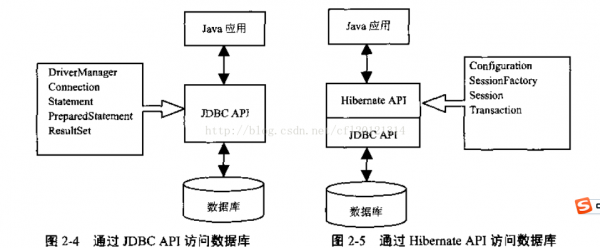
所以回头看看,其实从大体上,hibernate也只是在jdbc的封装,简化我们直接操作jdbc
的进程。在java这里,jdbc还是最为原始的最为直接的方式,不能说这个方法不好,由于当下
流行ibatis也是针对实体来创建不同的sql语句来做的,所以直接原始的方法也是有它的好处
的,比如:灵活、效力高。换过来,hibernate在jdbc的基础之上的封装,也避免了程序猿们
来直接去书写繁琐的sql语句和事务保护和缓存控制,另外开源也是1个方面。
固然这里对hibernate原理的讲授只是hibernate的冰山1角。后面,例如hibernate的缓存、3态、和对实体关联的处理、事务都是需要好好研究的。

