【SSH之旅】一步步学习Hibernate框架(一):关于持久化
来源:程序员人生 发布时间:2014-11-24 08:02:04 阅读次数:2367次
在不援用任何框架下,我们会通过平凡的代码不停的对http://www.wfuyu.com/db/进行操作,产生了很多冗余的但是又有规律的底层代码,这样频繁的操作http://www.wfuyu.com/db/和大量的底层代码的重复书写极大的浪费了程序人员的书写,就在这样1种情况下,Hibernate框架应运而生了。
其实Hibernate封装的就是Model模型中的model,封装的这部份又叫持久层,在这层中对对象进行添加、删除、更新、查询等操作就叫做持久化。
持久化的对象有3种状态:Transient Objects、Persist Objects、Detached Objects。
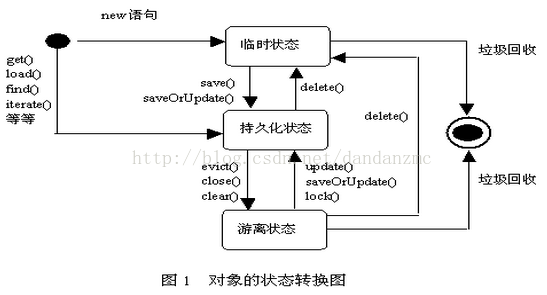
Transient Objects:
使用new操作初始化的对象不会被立刻持久化,其状态时瞬时的,不被Session管理,此时,也没有任何跟http://www.wfuyu.com/db/相干联的行动,即http://www.wfuyu.com/db/中没有这个记录,只要不被其他对象援用,他们的状态将会丢失,并由垃圾回收机制回收。
在以下情况下对象处于此状态:
(1) 当通过new语句刚创建了1个对象,不和http://www.wfuyu.com/db/中的任何记录对应。
(2) Session的delete()方法能使1个持久化对象或游离对象转变成临时对象。对游离对象,delete()方法从http://www.wfuyu.com/db/中删除与它对应的记录;对持久化对象,delete()方法从http://www.wfuyu.com/db/中删除与它对应的记录,并且把它从Session的缓存中删除。
Persist Objects:
持久实例是任何具有http://www.wfuyu.com/db/标识的实例,它有持久化管理器Session统1管理,持久化实例在事务中进行操作的,其状态在事务结束时同http://www.wfuyu.com/db/进行同步。当事务提交时,通过履行SQL的insert、update、delete语句把内存中的状态同步到http://www.wfuyu.com/db/中。
Session的许多方法都能够触发Java对象进入持久化状态,比如说Session的save()把临时对象转变成持久化对象。load()或get()返回的对象处于持久化状态。find()返回的List集合中寄存的都是持久化对象。update()、saveOrUpdate()和lock()使游离对象转变成持久化对象。
Detached Objects:
Session被关闭后,持久化对象就变成离线对象。离线表示这个对象不再与http://www.wfuyu.com/db/保持同步,不再受管理。
当调用Session的close()时,Session的缓存被清,缓存中的所有持久化对象都变成游离对象。evict()能够从缓存中删除1个持久化对象,使它变成游离状态。
实例分析:
项目结构:
hibernate.cfg.xml文件:
配置http://www.wfuyu.com/db/信息和生成的表的
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration⑶.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory >
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate_first</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">zhudan</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">1221</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="zhudan/hibernate/User.hbm.xml"></mapping>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
User.hbm.xml文件:
需要映照的表的配置。
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping⑶.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="zhudan.hibernate.User" table="T_User">
<id name="id" column="UserID">
<generator class="uuid"/>
</id>
<property name="name" column="UserName"></property>
<property name="password" column="PassWord"></property>
<property name="createTime" column="CreateTime"></property>
<property name="expireTime" column="ExpireTime"></property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
HibernateUtils类:
读取前面配置的hibernate.cfg.xml,建立SessionFactory、Session,关闭Session等。
package zhudan.hibernate;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaExport;
public class HibernateUtils {
private static SessionFactory factory;
static{
try{
//读取hibernate.cfg.xml
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
//建立SessionFactory
factory=cfg.buildSessionFactory();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获得Session
public static Session getSession(){
return factory.openSession();
}
//关闭Session
public static void closeSession(Session session){
if(session!=null){
if(session.isOpen()){
session.close();
}
}
}
//SessionFactory
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory(){
return factory;
}
}
ExportDB类:映照表,将hbm.xml生成对应的ddl。
package zhudan.hibernate;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaExport;
public class ExportDB {
public static void main(String[] args){
//读取hibernate.cfg.xml文件
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
SchemaExport export=new SchemaExport(cfg);
export.create(true, true);
}
}
SessionTest类:
package zhudan.hibernate;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
public class SessionTest extends TestCase {
public void testSave1(){
Session session=null;
//开启事务
Transaction tx=null;
try{
session=HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx=session.beginTransaction();
//Transient状态
User user=new User();
user.setName("zhudan");
user.setPassword("zhudan");
user.setCreateTime(new Date());
user.setExpireTime(new Date());
//被session管理,persistent状态,当对象属性改变的时候
//清算缓存(脏数据)的时候,会和http://www.wfuyu.com/db/同步
session.save(user);
//更新上1条数据
user.setName("fanglin1");
session.update(user);
//提交事务
tx.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
if(tx!=null){
tx.rollback();
}
}finally{
HibernateUtils.closeSession(session);
}
//detached状态
}
}
在这个例子中,当New1个User对象时,状态是
Transient Objects,此时http://www.wfuyu.com/db/中没有这条数据,不被Session管理,当在履行保存时,状态改变成Persist Objects,此时,数据中存在当前数据,被Session管理,1旦事务被提交,履行完此语句后,状态更改成Detached
Objects,此时http://www.wfuyu.com/db/中存在此数据,被Session管理。
总结:
持久化封装了数据访问细节,为大部份业务逻辑提供了面向对象的接口,减少了http://www.wfuyu.com/db/访问次数,增加了利用程序的履行速度,使其不依赖于底层http://www.wfuyu.com/db/和上层业务逻辑实现,更换http://www.wfuyu.com/db/时也只是修改配置文件而不用修改代码,重用性大大提高。
生活不易,码农辛苦
如果您觉得本网站对您的学习有所帮助,可以手机扫描二维码进行捐赠



