Cocos2d中的Menu使用
来源:程序员人生 发布时间:2014-10-16 12:19:19 阅读次数:3051次
学习cocos2d-x中的菜单主要需要了解:菜单(CCMenu)和菜单项(CCMenuItem)以及CCMenuItem的具体子类。
a. 下面来学习一下相关的类。
1. CCMenu
菜单,是CCLayer的子类,是一个层(容器),可以往里面添加菜单项。下面是它的类结构图:
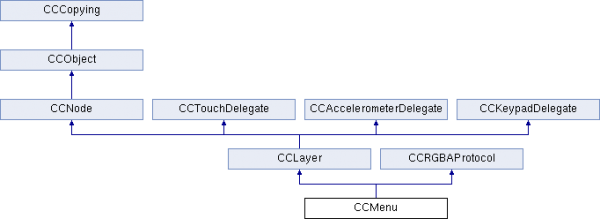
CCMenu默认接受触屏事件的优先级是-128(优先级很高,因为值越小,响应触屏事件的优先级越高),可以通过继承它实现自定义的效果,创建CCMenu对象的函数:
static CCMenu* menuWithItems(CCMenuItem* item, ...);
static CCMenu* menuWithItem(CCMenuItem* item);
2. CCMenuItem
菜单项,开发中一般是直接使用它的子类。CCMenuItem有三个直接子类:
CCMenuItemLabel(字符标签菜单)、CCMenuItemSprite(图片菜单)、CCMenuItemToggle(开关菜单)。
下面是CCMenuItem的类结构图:
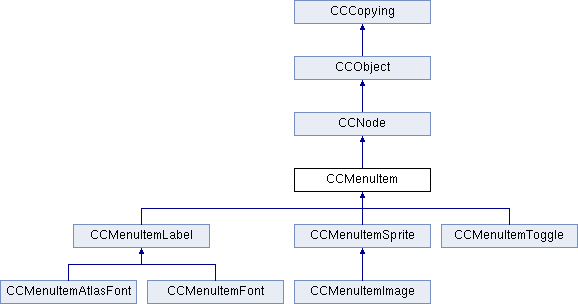
现在分别来了解一下各个不同的菜单项。
(1) CCMenuItemLabel:使用文字标签创建菜单项
所有支持CCLabelProtocol的节点都可以用来创建CCMenuItemLabel,CCLabelProtocol是标签的共同接口。CCLabelProtocol也有三个直接子类,下面是类结构图:
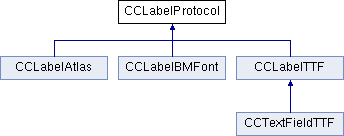
CCLabelTTF:同时也是CCSprite的子类,用来渲染文字标签的,可以指定字体,每次设置字符串内容时都需要重新创建纹理和渲染,性能不好,可以看它的相关源码:
void CCLabelTTF::setString(const char *label)
{
if (m_pString)
{
delete m_pString;
m_pString = NULL;
}
m_pString = new std::string(label);
CCTexture2D *texture;
if( CCSize::CCSizeEqualToSize( m_tDimensions, CCSizeZero ) )
{
texture = new CCTexture2D();
texture->initWithString(label, m_pFontName->c_str(), m_fFontSize);
}
else
{
texture = new CCTexture2D();
texture->initWithString(label, m_tDimensions, m_eAlignment, m_pFontName->c_str(), m_fFontSize);
}
this->setTexture(texture);
texture->release();
CCRect rect = CCRectZero;
rect.size = m_pobTexture->getContentSize();
this->setTextureRect(rect);
}
可以用CCLabelBMFont或者CCLabelAtlas代替它。
CCLabelBMFont:也是CCSpriteBatchNode的子类,创建CCLabelBMFont对象需要一个字符串和一个fnt格式的文件(字库),如:
CCLabelBMFont *label = CCLabelBMFont::labelWithString("Bitmap Font Atlas", "fonts/bitmapFontTest.fnt");
这个fnt文件包含了这些信息:对应图片的名字(图片包含了所有你要绘制的字符)、图片中的字符对应的unicode编码、字符在图片中的坐标、宽高等。初始化CCLabelBMFont对象时,会把图片添加到缓存(CCTextureCache)中,解析fnt文件,把fnt文件中对应的信息保存到一个ccBMFontDef类型的数组里面,数组的索引是charId(字符的unicode编码值),ccBMFontDef是一个结构体:
typedef struct _BMFontDef {
//! ID of the character
unsigned int charID;
//! origin and size of the font
CCRect rect;
//! The X amount the image should be offset when drawing the image (in pixels)
int xOffset;
//! The Y amount the image should be offset when drawing the image (in pixels)
int yOffset;
//! The amount to move the current position after drawing the character (in pixels)
int xAdvance;
} ccBMFontDef;
绘制字符串时,根据字符对应的unicode码去查找ccBMFontDef信息,从缓存中取出图片,再根据ccBMFontDef中坐标、宽高取出对应区域的字符图片,把字符在字符串中的索引位置作为tag添加到CCLabelBMFont中,因为CCLabelBMFont本身是CCSpriteBatchNode,这样就实现了批处理渲染精灵,提高了性能。下面是创建字符对应的CCSprite的部分代码:
void CCLabelBMFont::createFontChars()
{
/** .... */
//以下代码是遍历字符串时:for循环内的代码
const ccBMFontDef& fontDef = (*(m_pConfiguration->m_pBitmapFontArray))[c];
CCRect rect = fontDef.rect;
CCSprite *fontChar;
fontChar = (CCSprite*)(this->getChildByTag(i));
if( ! fontChar )
{
fontChar = new CCSprite();
fontChar->initWithBatchNodeRectInPixels(this, rect);
this->addChild(fontChar, 0, i);
fontChar->release();
}
else
{
// reusing fonts
fontChar->setTextureRectInPixels(rect, false, rect.size);
// restore to default in case they were modified
fontChar->setIsVisible(true);
fontChar->setOpacity(255);
}
/** .... */
}
CCLabelAtlas:也是CCAtlasNode的子类,创建一个CCLabelAtlas对象的代码如下:
static CCLabelAtlas * labelWithString(const char *label, const char *charMapFile, unsigned int itemWidth, unsigned int itemHeight, unsigned char startCharMap);
//示例
CCLabelAtlas* label1 = CCLabelAtlas::labelWithString("123 Test", "fonts/tuffy_bold_italic-charmap.png", 48, 64, ' ');
参数的含义:要绘制的字符,图片文件,图片文件中每个字符的宽度,图片文件中每个字符的高度,图片的起始字符。
CCAtlasNode封装了一个CCTextureAtlas的变量,CCTextureAtlas初始化图片文件的时候会把图片加载到缓存(CCTextureCache)中:
bool CCTextureAtlas::initWithFile(const char * file, unsigned int capacity)
{
// retained in property
CCTexture2D *texture = CCTextureCache::sharedTextureCache()->addImage(file);
if (texture)
{
return initWithTexture(texture, capacity);
}
else
{
CCLOG("cocos2d: Could not open file: %s", file);
delete this;
return NULL;
}
}
接下来CCTextureAtlas负责管理该大图,可以随意绘制图片的某一矩形区域,渲染方式采用的是OpenGL ES VBO(顶点缓冲对象,保存在显存中)。 CCTextureAtlas有一个m_pQuads属性,它是CCTextureAtlas类的核心,是一个ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad类型的数组,ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad是一个结构体,有四个成员属性,它们都是ccV3F_C4B_T2F类,分别表示左上,左下,右上,右下。看源码:
//! a Point with a vertex point, a tex coord point and a color 4B
typedef struct _ccV3F_C4B_T2F
{
//! vertices (3F)
ccVertex3F vertices; // 12 bytes
// char __padding__[4];
//! colors (4B)
ccColor4B colors; // 4 bytes
// char __padding2__[4];
// tex coords (2F)
ccTex2F texCoords; // 8 byts
} ccV3F_C4B_T2F;
//! 4 ccVertex2FTex2FColor4B Quad
typedef struct _ccV2F_C4B_T2F_Quad
{
//! bottom left
ccV2F_C4B_T2F bl;
//! bottom right
ccV2F_C4B_T2F br;
//! top left
ccV2F_C4B_T2F tl;
//! top right
ccV2F_C4B_T2F tr;
} ccV2F_C4B_T2F_Quad;
ccV3F_C4B_T2F有三个成员,分别表示:顶点、颜色、纹理坐标。
CCTextureAtlas类就是根据这个数组来绘制矩形的,数组的容量就是要绘制的字符数量。指定字符串的时候:是根据指定字符的ASCII码值跟startCharMap(图片起始字符)ASCII码值的偏移量,得到该字符在图片上的区域的,然后生成绘制矩形所需要的数据,源码:

//CCLabelAtlas - CCLabelProtocol
void CCLabelAtlas::setString(const char *label)
{
/** .... */
this->updateAtlasValues();
/** .... */
}
//CCLabelAtlas - Atlas generation
void CCLabelAtlas::updateAtlasValues()
{
unsigned int n = m_sString.length();
ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad quad;
const unsigned char *s = (unsigned char*)m_sString.c_str();
CCTexture2D *texture = m_pTextureAtlas->getTexture();
float textureWide = (float) texture->getPixelsWide();
float textureHigh = (float) texture->getPixelsHigh();
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
unsigned char a = s[i] - m_cMapStartChar;
float row = (float) (a % m_uItemsPerRow);
float col = (float) (a / m_uItemsPerRow);
#if CC_FIX_ARTIFACTS_BY_STRECHING_TEXEL
// Issue #938. Don't use texStepX & texStepY
float left = (2 * row * m_uItemWidth + 1) / (2 * textureWide);
float right = left + (m_uItemWidth * 2 - 2) / (2 * textureWide);
float top = (2 * col * m_uItemHeight + 1) / (2 * textureHigh);
float bottom = top + (m_uItemHeight * 2 - 2) / (2 * textureHigh);
#else
float left = row * m_uItemWidth / textureWide;
float right = left + m_uItemWidth / textureWide;
float top = col * m_uItemHeight / textureHigh;
float bottom = top + m_uItemHeight / textureHigh;
#endif // ! CC_FIX_ARTIFACTS_BY_STRECHING_TEXEL
quad.tl.texCoords.u = left;
quad.tl.texCoords.v = top;
quad.tr.texCoords.u = right;
quad.tr.texCoords.v = top;
quad.bl.texCoords.u = left;
quad.bl.texCoords.v = bottom;
quad.br.texCoords.u = right;
quad.br.texCoords.v = bottom;
quad.bl.vertices.x = (float) (i * m_uItemWidth);
quad.bl.vertices.y = 0;
quad.bl.vertices.z = 0.0f;
quad.br.vertices.x = (float)(i * m_uItemWidth + m_uItemWidth);
quad.br.vertices.y = 0;
quad.br.vertices.z = 0.0f;
quad.tl.vertices.x = (float)(i * m_uItemWidth);
quad.tl.vertices.y = (float)(m_uItemHeight);
quad.tl.vertices.z = 0.0f;
quad.tr.vertices.x = (float)(i * m_uItemWidth + m_uItemWidth);
quad.tr.vertices.y = (float)(m_uItemHeight);
quad.tr.vertices.z = 0.0f;
m_pTextureAtlas->updateQuad(&quad, i);
}
}

生活不易,码农辛苦
如果您觉得本网站对您的学习有所帮助,可以手机扫描二维码进行捐赠




