Explain
红黑树是每个节点都带有颜色属性的二叉查找树,颜色为红色或黑色。在二叉查找树强制一般要求以外,对于任何有效的红黑树我们增加了如下的额外要求:
性质1. 节点是红色或黑色。
性质2. 根是黑色。
性质3. 所有叶子都是黑色(叶子是NIL节点)。
性质4. 每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色。(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
性质5. 从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有简单路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
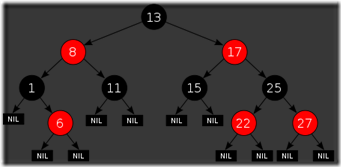
这些约束强制了红黑树的关键性质: 从根到叶子的最长的可能路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长(性质4 保证了路径最长的情况为一红一黑,最短的情况为全黑,再结合性质5,可以推导出)。结果是这个树大致上是平衡的。因为操作比如插入、删除和查找某个值的最坏情况时间都要求与树的高度成比例,这个在高度上的理论上限允许红黑树在最坏情况下都是高效的,而不同于普通的二叉查找树。
红黑树结构定义:
/* * RBTree.h * * Created on: Sep 25, 2014 * Author: root */ #ifndef RBTREE_H_ #define RBTREE_H_ typedef unsigned long rbtree_key_t; typedef long rbtree_key_int_t; struct rbtree_node_t { rbtree_key_t key; //key rbtree_node_t *left; //左子树 rbtree_node_t *right; //右子树 rbtree_node_t *parent; //父节点 unsigned char color; //颜色 }; struct rbtree_t { rbtree_node_t *root; //根节点 rbtree_node_t *sentinel; //哨兵 }; #endif /* RBTREE_H_ */
二、树的旋转知识
1.左旋
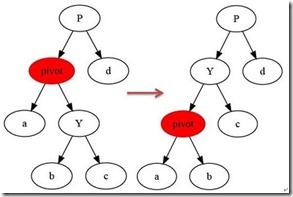
如上图所示:
当在某个结点pivot上,做左旋操作时,我们假设它的右孩子y不是NIL[T],pivot可以为树内任意右孩子而不是NIL[T]的结点。
左旋以pivot到y之间的链为“支轴”进行,它使y成为该孩子树新的根,而y的左孩子b则成为pivot的右孩子。
伪代码图解:

实现代码:
void RBTree::rbtree_left_rotate( rbtree_node_t* node_x) { rbtree_node_t *node_y; rbtree_node_t **root = & m_rbtree. root; rbtree_node_t *sentinel = m_rbtree. sentinel; node_y = node_x-> right; //Setp 1. 设置y node_x-> right = node_y-> left; //Step 2 .将y 的左子树变为x的右子树 if(node_y-> left != sentinel) { node_y-> left-> parent = node_x; } node_y-> parent = node_x-> parent; //Step 3. 设置y的父亲 if(node_x == *root) //空树,将y设为根 { *root = node_y; } else if(node_x == node_x->parent ->left ) //x为左子树,将y放在x父节点的左子树 { node_x-> parent-> left = node_y; } else //x为右子树,将y放在x父节点的右子树 { node_x-> parent-> right = node_y; } node_y-> left = node_x; //Step4.将x链到y的左子树 node_x-> parent = node_y; }
2.右旋
伪代码图解:

实现代码:
void rb_tree::rbtree_right_rotate( rbtree_node_t *node_x) { rbtree_node_t *node_y; rbtree_node_t **root = & m_rbtree. root; rbtree_node_t *sentinel = m_rbtree. sentinel; node_y = node_x-> left; //Step 1. 设置y node_x-> left = node_y-> right; //Step 2.将y的右子树变为x的左子树 if( node_y-> right != sentinel) { node_y-> right-> parent = node_x; } node_y-> parent = node_x-> parent; if( node_x == *root) //Step 3.若x为根,设置y为跟 { *root = node_y; } else if( node_x == node_x->parent ->right ) //x在右子树,y设置在右子树 { node_x-> parent-> right = node_y; } else //x在左子树,y设置在左子树 { node_x-> parent-> left = node_y; } node_y-> right = node_x; //Step 4.将x链接在y的右子树 node_x-> parent = node_y; }
三、红黑树的插入
红黑树的插入和二叉树的相似,都是如果左子树小,向左子树搜索,否则向右子树搜索,不同的红黑树插入完需要调整,恢复红黑树的特性,伪代码如下 :
RB-INSERT(T,z) y <- NIL[T] //Step 1.将y设置为哨兵,将x设置为根 x <- root[T] while x!=NIL[T] //Step 2.搜索,如果z比x小,向左子树搜索,否则向右子树搜索,y插入位置 do y <- x if key[z] < key[x] then x <- left[x] else x <- right[x] p[z] <- y if y=NIL[T] //Step 3.若为空树,z为根, then root[T] <- z else if key[z] < key[y] //若z比y小,z放在y的左子树 then left[y] <- z else right[y] <- z //否则,z放在y的右子树 left[z] <- NIL[T] right[z] <- NIL[T] //Step 4.将z左右子树设置为哨兵,颜色设置为红色 color[z] <- RED RB-INSERT-FIXUP(T,z) //Step 5.红黑树调整
实现代码:
void RBTree::rbtree_insert( rbtree_node_t *node_z) { rbtree_node_t *node_y = m_rbtree. sentinel; //Step 1.将y设置为哨兵,将x设置为根 rbtree_node_t *node_x = m_rbtree.root; if(m_rbtree.root== m_rbtree. sentinel) //若为空树,z为根, { node_z-> parent = NULL; node_z-> left = m_rbtree. sentinel; node_z-> right = m_rbtree. sentinel; rbt_black(node_z); m_rbtree.root = node_z; return; } for(;node_x != m_rbtree.sentinel;) //Step 2.搜索,如果z比x小,向左子树搜索,否则向右子树搜索,y插入位置 { node_y = node_x; node_x = node_z->key - node_x->key < 0 ? node_x->left:node_x->right; } node_z->parent = node_y; if(node_z->key - node_y->key < 0) //Step 3 若z比y小,z放在y的左子树 { node_y->left = node_z; } else //否则,z放在y的右子树 { node_y->right = node_z; } node_z-> left = m_rbtree. sentinel; //Step 4.将z左右子树设置为哨兵,颜色设置为红色 node_z-> right = m_rbtree. sentinel; rbt_red(node_z); //re-balance tree rbtree_insert_fixup(node); //Step 5.红黑树调整 }
红黑树插入调整伪代码:
RB-INSERT-FIXUP(T,z) while color[p[z]]=RED do if p[z]=left[p[p[z]]] then y <- right[p[p[z]]] if color[y]=RED then color[y] <- BLACK //情况1,z的叔叔y是红色 color[p[z]] <- BLACK color[p[p[z]]] <- RED z <- p[p[z]] else if z=right[p[z]] //情况2,z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是右孩子 then z <- p[z] LEFT-ROTATE(T,z) color[p[z]] <- BLACK // 情况3,z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是左孩子 color[p[p[z]]] <- RED RIGHT-ROTATE(T,p[p[z]]) else (same as then clause with “right” and “left” exchanged) color[root[T]] <- BLACK
情况1:z的叔叔y是红色
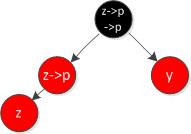
违反性质4,z和z的父亲都是红色。
调整方法:
首先将z->p涂黑,再将z->p->p涂红,最后将y涂黑。将z->p的颜色和z->p->p的颜色对换一下,再将y涂黑,其实是把z->p->p的黑色分发到两个红色儿子结点中,而其自身变为红色,维持了性质5,即维护了所有路径黑结点数量的一致性。这里要提出的一个小细节是,红色结点变黑色不用考虑结点颜色冲突,而黑色结点变红色则要考虑结点颜色冲突,红变黑,随意变,黑变红,看冲突(不考虑性质5的前提下)。因为z->p->p是由黑色变红的,这时将z指向z->p->p,如果不出现结点颜色冲突的情况则完成修复,有颜色冲突则进入下一轮循环。
情况2:z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是右孩子
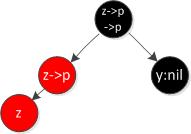
违反性质4,z和z的父亲都是红色。
调整方法:
首先也是将z->p涂黑,z->p->p涂红,这时候,我们就会发现根结点到y结点路径中的黑结点数目减少了1,我们再回顾一下前面对左旋、右旋方法的介绍,那么我们会发现,左旋、右旋的意义就在于此了:RIGHT-ROTATE(T,z->p->p)后,为根结点到y结点的路径上增加了一个黑色结点z->p,为根结点到z结点的路径上减少了一个红色结点z->p->p,一条路径增加黑色结点,另一条路径减少红色结点,insert就这样被修复了。
情况3:z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是左孩子
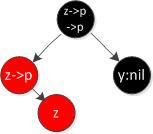
违反性质4,z和z的父亲都是红色。
调整方法:
将z->p涂黑,z->p->p涂红,这时候,想对红黑树进行修复的话,你会想到什么呢?和case 3一样直接RIGHT-ROTATE(T,z->p->p)么,如果直接RIGHT-ROTATE(T,z->p->p)的话,红色结点z将变成红色结点z->p->p的左儿子,其实是做了无用功。那我们就想办法把它变成case 3的那种形式吧,LEFT-ROTATE(T,z),很容易想到吧,LEFT-ROTATE(T,z)之后z,z->p,z->p->p又变成了我们喜闻乐见的三点一线的形式,也就是case 3。
实现代码:
void RBTree::rbtree_insert_fixup( rbtree_node_t *node_z) { rbtree_node_t **root = & m_rbtree. root; rbtree_node_t *node_y; while( node_z != *root && rbt_is_red(node_z-> parent)) { if(node_z-> parent == node_z->parent->parent->left) { node_y = node_z->parent->parent->right; //case1:z的叔叔y是红色 if(rbt_is_red(node_y)) { rbt_black( node_z->parent); rbt_black(node_y); rbt_red( node_z->parent->parent); node_z = node_z ->parent ->parent ; } else { //case2:z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是右孩子 if(node_z == node_z->parent->right) { node_z = node_z ->parent ; rbtree_left_rotate( node_z); } rbt_black( node_z->parent); rbt_red( node_z->parent->parent); rbtree_right_rotate( node_z); } } else { node_y = node_z->parent->parent->left; //case1:z的叔叔y是红色 if(rbt_is_red(node_y)) { rbt_black( node_z->parent); rbt_black(node_y); rbt_red( node_z->parent->parent); node_z = node_z ->parent ->parent ; } else { //case2:z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是左孩子 if(node_z == node_z->parent->left) { node_z =node_z ->parent ; rbtree_right_rotate( node_z); } rbt_black( node_z->parent); rbt_red( node_z->parent->parent); rbtree_left_rotate( node_z->parent->parent); } } } rbt_black(*root); }
四、红黑树的删除
删除的节点按照儿子的个数可以分为三种:
OK,回到红黑树上来。算法导论一书,给的红黑树结点删除的算法实现是:
RB-DELETE(T, z) if left[z] = nil[T] or right[z] = nil[T] //没有或者有一个儿子 then y ← z else y ← TREE-SUCCESSOR(z) //有两个儿子,取左子树的最大节点或右子树的最小节点 if left[y] ≠ nil[T] then x ← left[y] else x ← right[y] p[x] ← p[y] if p[y] = nil[T] //要删除的为根角点,则直接用x替代根节点 then root[T] ← x else if y = left[p[y]] //要删除的节点在左子树,则x放在在左子树 then left[p[y]] ← x else right[p[y]] ← x //要删除的节点在右子树,则x放在在右子树 if y ≠ z //z有两个儿子 then key[z] ← key[y] //将y的数据给z,实际上是删除的右子树的最小节点,然后把这个节点的数据拷到了z的位置 copy y's satellite data into z if color[y] = BLACK //设置y的颜色为黑色 then RB-DELETE-FIXUP(T, x) return y
实现代码:
void RBTree::rbtree_delete( rbtree_node_t *node_z) { rbtree_node_t **root =& m_rbtree. root; rbtree_node_t *sentinel = m_rbtree. sentinel; rbtree_node_t *node_y; //the node to replace node_z rbtree_node_t *node_x; //node_y's child bool is_node_y_red = false; if(node_z-> left == sentinel) { node_x = node_z-> right; node_y = node_z; } else if(node_z->right == sentinel) { node_x = node_z-> left; node_y = node_z; } else { node_y = rbtree_min(node_z-> right); if(node_y->left != sentinel) { node_x = node_y-> left; } else { node_x = node_y-> right; } } //the node to delete is root if(node_y == *root) { *root = node_x; rbt_black(node_x); node_z->left = NULL; node_z->right = NULL; node_z->parent = NULL; node_z->key = 0; return; } is_node_y_red = rbt_is_red(node_y); //Link node_y's child node_x to node_y's parent if(node_y == node_y-> parent-> left) { node_y-> parent-> left = node_x; } else { node_y-> parent-> right = node_x; } if(node_y == node_z) { node_x-> parent = node_y-> parent; } else { if(node_y->parent == node_z) { node_x-> parent = node_y; } else { node_x-> parent = node_y-> parent; } //replace node_z with node_y,include color,so the place of node_z is not change node_y-> left = node_z-> left; node_y-> right = node_z-> right; node_y-> parent = node_z-> parent; rbt_copy_color(node_y,node_z); //the node to delete is root if( node_z == *root) { *root = node_y; } else { if(node_z == node_z->parent ->left ) { node_z-> parent-> left = node_y; } else { node_z-> parent-> right = node_y; } } if(node_z->left != sentinel) { node_y-> left-> parent = node_y; } if(node_z->right != sentinel) { node_y-> right-> parent = node_y; } } node_z->left = NULL; node_z->right = NULL; node_z->parent = NULL; node_z->key = 0; //if node_y is a black node,the action move node_y to replace node_z change the struct of rbtree if(!is_node_y_red) { rbtree_delete_fixup(node_x); } }
生活不易,码农辛苦
如果您觉得本网站对您的学习有所帮助,可以手机扫描二维码进行捐赠
