一直知道Fragment很强大,但是一直都没有去学习,现在有些空闲的时间,所以就去学习了一下Fragment的简单入门。我也会把自己的学习过程写下来,如果有什么不足的地方希望大牛指正,共同进步!
一、Fragment简介
1.Fragment作为Activity界面的一部分组成出现;
2.可以在一个Activity中同时出现多个Fragment,并且,一个Fragment亦可在多个Activity中使用;
3.在Activity运行过程中,可以添加、移除或者替换Fragment(add()、remove()、replace());
4.Fragment可以响应自己的输入事件,并且有自己的生命周期,当然,它们的生命周期直接被其所属的activity的生命周期影响。
那我们为什么要用Fragment呢?主要目的是用在大屏幕设备上--例如平板电脑上,支持更加动态和灵活的UI设计。平板电脑的屏幕要比手机的大得多,有更多的空间来放更多的UI组件,并且这些组件之间会产生更多的交互。我们可以把Fragment认为是“小的Activity”,Fragment更加简洁。
二、Fragment的简单使用
那我们就简单的显示2个Fragment为例来讲解一下。
1.在XML中添加Fragment:
新建Fragment1、Fragment2(注意:这里可能有2个包可以选择导入android.app.Fragment或android.support.v4.app.Fragment都是可以的,我这里选择使用了前者,但是两者使用时有区别的,在结尾中我会讲到):
Fragment1代码:
package com.example.fragment;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import com.example.fragmentdemo.R;
public class Fragment1 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.e("TAG", "in");
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false);
}
}
Fragment2代码:
package com.example.fragment;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import com.example.fragmentdemo.R;
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
}
}
Fragment1的xml代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FF69B4"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="这是第一个Fragment" />
</LinearLayout>
Fragment2的xml代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#EECBAD"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="这是第二个Fragment" />
</LinearLayout>
我们在activity_main.xml中添加两个Fragment,代码如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:baselineAligned="false" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:name="com.example.fragment.Fragment1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment2"
android:name="com.example.fragment.Fragment2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity代码如下:
package com.example.fragmentdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
然后运行工程就可以显示Fragment了,下面是效果图。
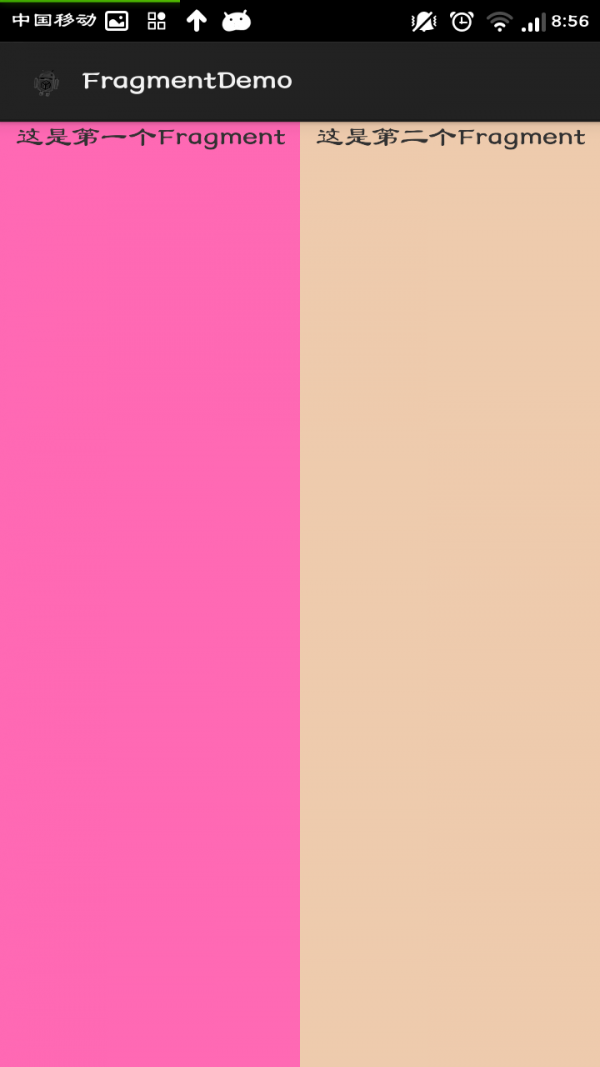
2.动态添加Fragment:
我们只需要修改MainActivity和activity_main.xml中的代码就可以了。
activity_main.xml代码:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" />
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity代码:
package com.example.fragmentdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import com.example.fragment.Fragment1;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.main, new Fragment1()).commit();
}
}
然后运行工程就可以动态的显示Fragment了,下面是效果图。

三、app包下和V4包下的Fragment的区别
1、尽量不要用app包中的fragment,因为这个是在3.0之后才有的,支持的版本太高,在低版本中是是用不了的;
2、android.support.v4.app.Fragment:可以兼容到1.6的版本;
3、关于这两个fragment使用<fragment>标签的问题:
(1)app.fragment和v4.fragment都是可以使用<fragment>标签的只是在在使用的时候如果是app.fragment则没有什么特殊的地方继承Activity即可。
(2)当v4.fragment使用<fragment>标签的时候就要特别注意了:当这个Activity的布局中有<fragment>标签的时候,这个Activity必须继承FragmentActivity,否则就会报错。此时如果不卜继成FragmentActivity的话
编译系统会把<fragment>认为是app包中的Fragment来处理。但是此时我们导入的是v4包中的FragmentAndroid官方文档中的Fragment的例子就是以app包中的Fragment来讲解的。
(3)app包中关于Fragment的类和方法在V4包中都是有相应的对应的。
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/a465456465/article/details/10415211,感谢。
上面就是Fragment的简单使用方法,Demo下载,下一节我会讲Fragment的详细使用。欢迎关注,我的博客园地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/getherBlog/p/3943547.html。


